CBIS.
advertisement

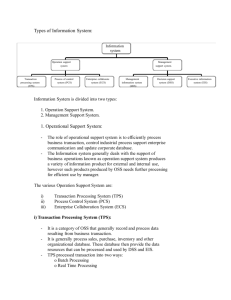
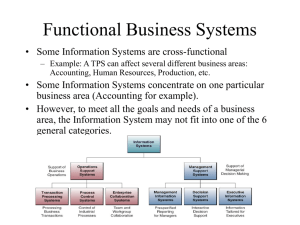
Computer Based Information System Rita Mallik Railway Information System Freight Operations Information System Passenger Reservation Systems (PRS) Unreserved Ticketing System (UTS) Coach Maintannce System E-Procurement System Parcel Magmt System Railway Wagons Identification(RFID) Track Management system IS for Indian Army Geo Information System Army Strategic Operational Information Dissemination System(ASTROIDS) Command Information and Decision Support System (CIDSS) Battlefield Support System (BSS) Artillery Combat Command and Control System (ACCCS) Air Defence Control and Reporting System (ADC&RS) LIC Information System Front-End Operation System INTERACTIVE VOICE RESPONSE SYSTEMS (IVRS) Electronic Bill Presentment & Payment (EBPP) Vi E-Trans service covers about 6,500 dedicated vehicles and nearly 20,000 other vehicles engaged in undertaking single trip. VI eTrans Pvt Ltd, a logistics service intermediary and a joint venture between Bharat Petroleum Corporation, Venture Infotek and Winex Trans. Winex Trans- Logistics & Transportation Bharat Petrolium-4500 terminals Venture Infotech- Business Cards Learning Objectives Information System concepts Define Information System types Functional Information System Information Infrastructure and different types of information Architectures Information system applications Information System Concepts Information System is one that collects, processes,stores, analyzes and dissiminates data and informtaion for a specific purpose. Difference in Information Needs • Top managers need information for planning, setting objectives, and making major strategic decisions. • Middle managers need information that helps them allocate resources and oversee the activities under their control. • First-line managers require information that helps them supervise employees, oversee daily operations, and coordinate activities. Classification of Information System Types of Information Systems Operations Support Systems Transaction processing systems Batch – transaction data accumulate over time, processed periodically. Real-time – data processed immediately after a transaction occurs. Process Control Systems – monitor & control physical processes. Enterprise Collaboration Systems Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) •Transaction processing systems are designed to process specific types of data input from ongoing transactions. TPSs can be manual, as when data is typed into a form on a screen, or automated by using scanners or sensors to capture data. • Organizational data is processed by a TPS—sales orders, payroll, accounting, financial, marketing, purchasing, inventory control, and so on. •Transactions are either: • Internal transactions: Transactions that originate from within the organization or that occur within the organization. Examples are payroll, purchases, budget transfers, and payments (in accounting terms, they’re referred to as accounts payable). • External transactions: Transactions that originate from outside the organization, for example, from customers, suppliers, regulators, distributors, and financing institutions 11 Transaction Processing System Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) 13 Management Information System (MIS) • The functional areas or departments— accounting, finance, production / operations, marketing and sales, human resource, and engineering and design— are supported by ISs designed for their particular reporting needs. Generalpurpose reporting systems are referred to as management information systems (MIS). Their objective is to provide reports to managers for tracking operations, monitoring, and control. 14 Management Information System (MIS) • Typically, a functional system provides reports about such topics as operational efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity by extracting information from databases and processing it according to the needs of the user. Types of reports are the following: 15 Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Decision support systems (DSS) are interactive applications that support decision making. Configurations of a DSS range from relatively simple applications that support a single user to complex enterprise-wide systems. • A DSS can support the analysis and solution of a specific problem, evaluate a strategic opportunity, or support ongoing operations. These systems support unstructured and semi structured decisions, such as whether to make or buy products and what new products to develop and introduce into existing markets. • Decisions range from structured to unstructured - Structured decisions are those that have a well-defined method for solving and the data needed to reach a decision. - An example of a structured decision is determining whether an applicant qualifies for an auto loan or whether to extend credit to a new customer— and the terms of those financing options. - Unstructured decisions that depend on human intelligence, knowledge, and/or experience—as well as data and models to solve. - Examples include deciding which new products to develop or which new markets to enter. 16 DSS DSS ... DSS Analysis: What-if Analysis - Goal Seeking Analysis -Sensitivity analysis - Optimization Analysis DSS Application: Planners Lab (plannerslab.com) 18 EIS -EIS provide extensive online analysis tools including trend analysis, exception reporting & "drill-down" capability . -Access a broad range of internal and external data -are particularly easy to use (typically mouse or touchscreen driven) -are used directly by executives without 19 assistance present EIS Facts.... -Many senior managers find that direct on-line access to organizational data is helpful. -Paul Frech, president of Lockheed-Georgia, monitors employee contributions to company-sponsored programs (United Way, blood drives) as a surrogate measure of employee morale (Houdeshel and Watson 1987). -C. Robert Kidder, CEO of Duracell, found that productivity problems were due to salespeople in Germany wasting time calling on small stores and took corrective action (Main 1989). Types of Information Systems (continued) Other Classifications Expert systems – expert advice Knowledge management systems – support the creation, organization, & dissemination of business knowledge Functional business systems – support the basic business functions Strategic information systems – strategic advantage Strategic Information System Alber Einstein once said “The significan problem we face canont be solved at the same level of thinking we were at when we created them” Strategic systems are information systems that are developed in response to corporate business initiative. They are intended to give competitive advantage to Strategies..... Porter's five force model Managerial challenges of information technology Information systems can be mismanaged and misapplied so that they create both technological and business failure. Top Five Reasons for Success Top Five Reasons for Failure User involvement Lack of user input Executive management support Proper planning Incomplete requirements and specifications Changing requirements and specifications Lack of executive support Realistic expectations Technological incompetence Clear statement of requirements