Aquifer presentation
advertisement

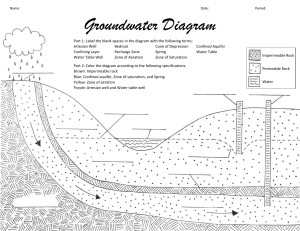
Aquifer A body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater Factors That Affect Groundwater Movement Porosity The amount of open spaces in rock or sediment Permeability The ability of a rock or sediment to let water pass through its pores and open spaces Parts of an Aquifer Zone of Aeration The zone that lies between the water table and the Earth’s surface Water Table The upper surface of underground water – the top of the zone of saturation Zone of Saturation The layer of an aquifer where the pore space is completely filled with water Permeable Layer Porous materials from which ground water can be extracted using a water well Impermeable Layer Dense material like clay or shale that stops groundwater from infiltrating further downward Confined Aquifer which has an impermeable dirt/rock layer that prevents water from seeping into the aquifer from the ground surface Unconfined Aquifer where water seeps from the ground surface directly above the aquifer Confined and unconfined aquifers Well, IT’S DEEP! Draw and color a diagram of an aquifer, include and label the following: Zone of Aeration, Zone of Saturation, Water Table, Lake or stream, Well, Confined aquifer, Unconfined aquifer, Permeable Layer, and Impermeable Layer. Analysis: 1. How can you tell where the water table is? 2. What do you notice about the level of the water in the well and the water table? 3. Why must the well be deeper than the water table? 4. What would happen to a basement built below the water table? 5. How does pollution of the surface of the land affect a well? 6. What property of water allows it to become polluted? 7. Why is clean water in wells important to the people in Utah? Conclusion: 2 things you learned: