File - Mrs. Dawson's Classroom
advertisement

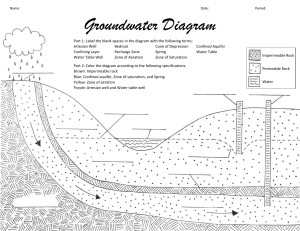
Journal #12 What is an aquifer? Where does water in an aquifer come from? Zones of Aquifers Gravity pulls water down through soil and rock layers until the water reaches impermeable rock. Water then begins to fill the spaces in the rock above the impermeable layer. As more water soaks into the ground, the water level rises underground to form 2 zones of groundwater. Zone of Saturation The layer of an aquifer where the pore space is completely filled with water is the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is the lower of the 2 zones of groundwater. The upper surface of the zone of saturation is called the water table. Zone of Aeration The zone that lies between the water table and Earth’s surface is called the zone of aeration. This zone is composed of three regions: Soil moisture region- uppermost region and holds water in top soil. Capillary fringe- the bottom region, just above the water table,. Water is drawn up from the zone of saturation into the capillary fridge similarly to how a towel draws up water from a spill This action is called capillary action. Movement of Ground Water Like water on Earth’s surface, groundwater flows downward in response to gravity. Water flows quickly through rock that highly permeable. The rate at which groundwater flows depends on the gradient Gradient- is the steepness of the slope As the gradient (slope) increases, the faster the water flows. Topography and the Water Table The depth of the water table depends on: Topography (arrangement of the land) The permeability of the aquifer Rate at which humans use the water During periods of prolonged rainfall, the water table rises What do you think happens during times of drought? Perched Water Table Only one water table exits in most areas In some areas, a layer of impermeable rock lies above the main water table. This rock prevents water from reaching the main zone of saturation. Water collects on top of this upper layer and creates a second water table called a perched water table. Conserving Groundwater In many areas, groundwater is the only source of fresh water. Communities often regulate the use of groundwater, discourage excess pumping, and recycle used water. Surface water enters an aquifer through an area called a recharge zone. Recharge zones are sensitive to pollution, as it can contaminate the entire aquifer. Your Assignment Draw a diagram of an aquifer. Use lots of color and give it a title (20 points) Label: ( 10 points each) Aquifer Zone of saturation Zone of aeration Water table Soil moisture region Capillary fringe Recharge zone Perched water table