The Properties of Water
advertisement

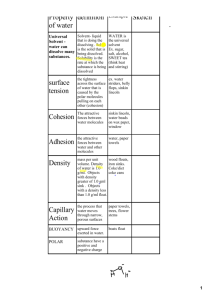
Water’s Unique Structure Like all matter, water is made up of atoms. Just as the 26 letters of the alphabet combine in different ways to form all the words in the English Language, about 100 types of atoms combine in different ways to form all types of matter. Atoms attach together, or bond, to form molecules. Water’s Unique Structure Two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom form a water molecule. A short way writing this is to use the chemical formula for water, H2O. Water’s Unique Structure Each end of the molecule has a slight electric charge. The oxygen end has a negative charge. The hydrogen ends has a positive charge. A molecule that has a electrically charged areas is called a polar molecule. Water’s Unique Structure The positive hydrogen ends of one water molecule attract the negative oxygen ends of nearby water molecules. As a result, the water molecules tend to stick together. Many of water’s unusual properties occur because of this attraction. Properties of Water Polarity Cohesion Adhesion Capillary Action Universal Solvent Surface Tension Density Specific Heat Polarity Polarity is an uneven distribution of charges across a water molecule. Water has unequal charges, therefore it is a polar molecule. It attracted to itself and other molecules carrying a charge. Polarity causes water to have all the other properties. Cohesion, Adhesion & Capillary Action Cohesion is when water molecules are attracted to other water molecules. Adhesion is when water molecules are attracted to other substances Capillary Action is when cohesion and adhesion is occurring and water molecules are moving through a substance http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oAY3yI Sf-24 Universal Solvent A solution is a mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another substance. The substance that does the dissolving is called a solvent. For example making lemonade from a powdered mix. Water is the solvent The two mixed together is the solution Universal Solvent Water is a universal solvent because it will dissolve anything with a charge (polar). The charged ends of the water molecule attract the molecules of other polar substances. If the substance does not have a charge water will not dissolve it. For example water/oil This property of water is one reason why water encountered on earth is rarely pure. Surface Tension Surface tension is the tightness across the surface of water that is caused by the polar molecules pulling on each other. The molecules at the surface are being pulled by the molecules next to them and below them. This pulling forces the surface of the water to have a curved shape. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=whukr452ZvY Density Density is referring to high tightly packed the molecules are. The density of water is 1.0 g/L Ice floats on water because it is less dense than water. Any substance that has a density less than 1.0 g/L will float. Any substance that has a density more than 1.0 g/L will sink. Specific Heat Specific heat is the amount of heat needed to move one gram of water one degree C. Water has a high specific heat. This means that it takes a long time for water to heat up and to cool down. For example the water temperature at the beach is always different the air temperature. Facts about Water Water is the only substance on Earth that occurs naturally as a solid, liquid and a gas. Water covers 71% of Earth’s surface. Most water 97% of it is not drinkable(saltwater). The majority of freshwater (3%) exits in ice caps, glaciers, and oceans. 77% of freshwater is frozen Of the 23% that is not frozen, approximately a .5% percent is available to supply living organisms with what they need to survive.