D.2: Digestion - SP New Moodle
advertisement

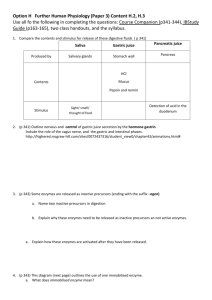
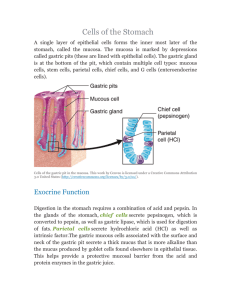
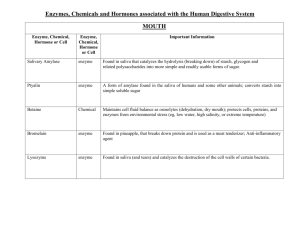
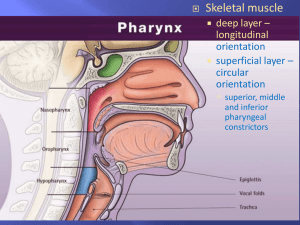
D.2: Digestion Review Draw and annotate the digestive system Nervous & hormonal control The volume and content of gastric secretions are controlled by nerves and hormones. The sight/smell of food causes the brain to stimulate a response via the vagus nerve from the medulla. Gland cells in the stomach are stimulated to secrete components of gastric juice. 1.Chemoreceptors in the stomach detect peptides or ‘stretch’ receptors detect distension of the stomach. 2.Impulses sent to the brain 3.Brain sends signal via the vagus nerve to endocrine cells in the duodenum wall & cells in the stomach (close to the duodenum) cells secrete gastrin. 4.The hormones gastrin stimulates the secretion of acid and pepsinogen. 5.The hormones secretin & somatostatin inhibit gastrin secretion if the pH of the stomach becomes to low. Exocrine secretions Salivary glands Gastric glands Pancreas Liver Intestinal glandular cells Water, electrolytes, salivary amylase, mucus, lysosome Water, mucus, enzymes inc. pepsin, rennin and hydrochloric acid Water, bicarbonate, enzymes inc. amylase, lipase, carboxypepidase, trypsinogen Bile, can be stored in the gall bladder. Emulsifies lipids (increases SA for lipase action) Variety of digestive enzymes Example of an exocrine gland Defined as ‘a collection of cells that produce and secrete a product which is then carried to a specific region of the body by a duct e.g. a digestive enzymes’ Exocrine glands often contain a lot of endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi bodies, vesicles/granules and mitochondria. Why? If the exocrine gland is producing enzymes, all of these things are required for protein synthesis, packaging and transportation Adaptations of the villus • Microvilli greatly increase surface area for absorption, face the lumen (interior of the SI). • Mitochondria provide the energy for active transport of molecules through the plasma membrane. • Pinocytotic vesicles are visible near the plasma membrane, pinocytosis is a form of active transport. • Tight junctions are membrane to membrane ‘seals’ between epithelial cells, this eliminates the possibility of molecules passing between the cells. Micrograph: villus epithelium 1. Google image search ‘ micrograph of villus epithelium’ 2. Screen shot the image into your notes 3. Identify and label: villus, mitochondrion, vesicles (hopefully you can see some), tight junction 4. What are the function of these organelles/structural components? Role of acid Acidic conditions of the stomach favor some hydrolysis reactions and help to control any pathogens present in ingested food. Acid is secreted by the parietal cells of the stomach. Acid denatures proteins, exposing polypeptides chains to the enzyme pepsin. Pepsin is released by chief cells as inactive pepsinogen. The acidic conditions converts pepsinogen pepsin. Defined as a defect in the lining of the stomach Research into stomach ulcers 1982 -1983, Dr Barry J. Marshall & Dr J. Robin Warren, proved the existence of Helicobacter pylori in the inner lining of the stomach. These bacteria secrete urease (creating ammonia) neutralising stomach acid, resulting in a habitable environment. More information page 675 Egestion Excretion of undigested materials. Fibre is not digested by the body. Rate materials move through the intestines is positively correlated with the amount of fibre present. DBQ page 677.