Enzymes, Chemicals and Hormones associated with the Human
advertisement
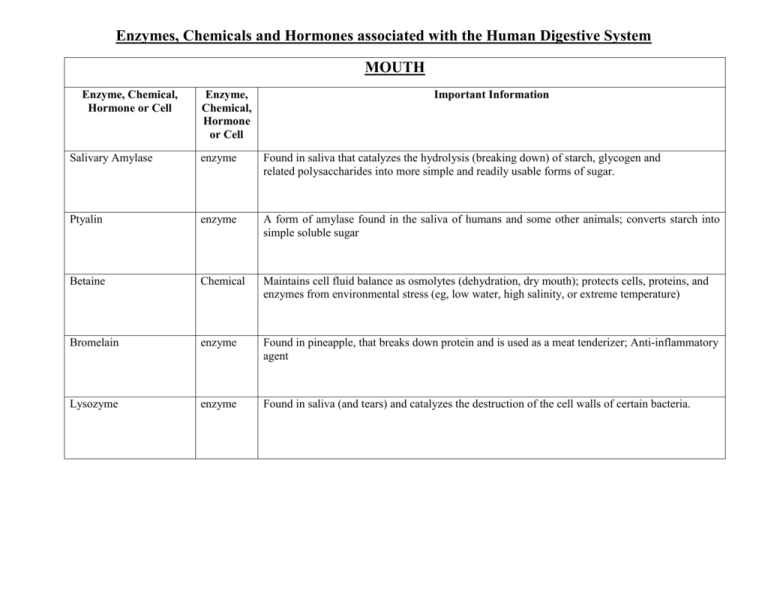
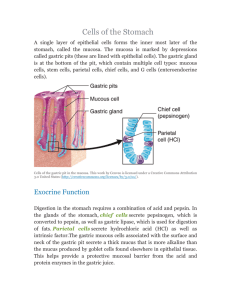
Enzymes, Chemicals and Hormones associated with the Human Digestive System MOUTH Enzyme, Chemical, Hormone or Cell Enzyme, Chemical, Hormone or Cell Important Information Salivary Amylase enzyme Found in saliva that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breaking down) of starch, glycogen and related polysaccharides into more simple and readily usable forms of sugar. Ptyalin enzyme A form of amylase found in the saliva of humans and some other animals; converts starch into simple soluble sugar Betaine Chemical Maintains cell fluid balance as osmolytes (dehydration, dry mouth); protects cells, proteins, and enzymes from environmental stress (eg, low water, high salinity, or extreme temperature) Bromelain enzyme Found in pineapple, that breaks down protein and is used as a meat tenderizer; Anti-inflammatory agent Lysozyme enzyme Found in saliva (and tears) and catalyzes the destruction of the cell walls of certain bacteria. STOMACH Enzyme, Chemical, Hormone or Cell Parietal Cells Enzyme, Chemical, Hormone or Cell cell Chief Cells cell Mucous neck or Pit Cells cell Involved in mucous production and are replaced every 2–4 days. This high rate of turnover is a protective mechanism designed to protect the epithelial lining of the stomach from both the action of pepsin and the acid produced by parietal cells; G Cells cell A gastrin-producing cell found in the antrum (initial portion of the pyloric portion of the stomach) of the stomach and to a lesser extent in the mucosa of the duodenum Pepsin enzyme R Released in the stomach as pepsinogen (zymogen - an inactive substance that is converted into an en enzyme when activated by another enzyme); the release of HCl stimulates the release of the basic m form of pepsin; when pepsinogen is exposed to HCl in the stomach the pepsinogen unfolds and pe breaks into pepsin; breaks down proteins into smaller polypeptides chemical ThThe pH of gastric (stomach) acid should normally be between 1.5-3.5, HCl denatures proteins; Aactivates the conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin; acts as antiseptic in the stomach; allows for improper mineral absorption as it assists in ionizing minerals HCl Important Information Are the stomach epithelium cells which secrete gastric acid (HCl); Primarily secreted in response to ingested protein or fat; stress also may stimulate acid output; also secrete intrinsic factor absorption of vitamin B12 and the normal development of red blood cells Pernicious anemia may be caused by the absence of intrinsic factor. Also called zymogenic cell. Any one of the columnar epithelial cells or the cuboidal epithelial cells that line the gastric glands and secrete pepsinogen which are needed for the digestion of proteins Intrinsic Factor Chemical A A substance secreted by the stomach that enables the body to absorb vitamin B12. It is a glycoprotein fd glycoprotein Gastrin hormone Gastrin is a major physiological regulator of gastric acid secretion. It also has an important growthpromoting influence on the gastric mucosa. Gastrin is synthesized in G cells, which are located in gastric pits, primarily in the antrum region of the stomach. Anticipation of food, stomach stretching (rugae), presence of partially digested food – stimulates the secretion of gastric juices rich in pepsin and HCl which aid in digestion.