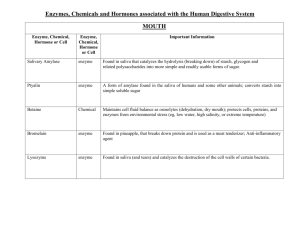
questions Opt h 2,3Further Human Physiology
advertisement
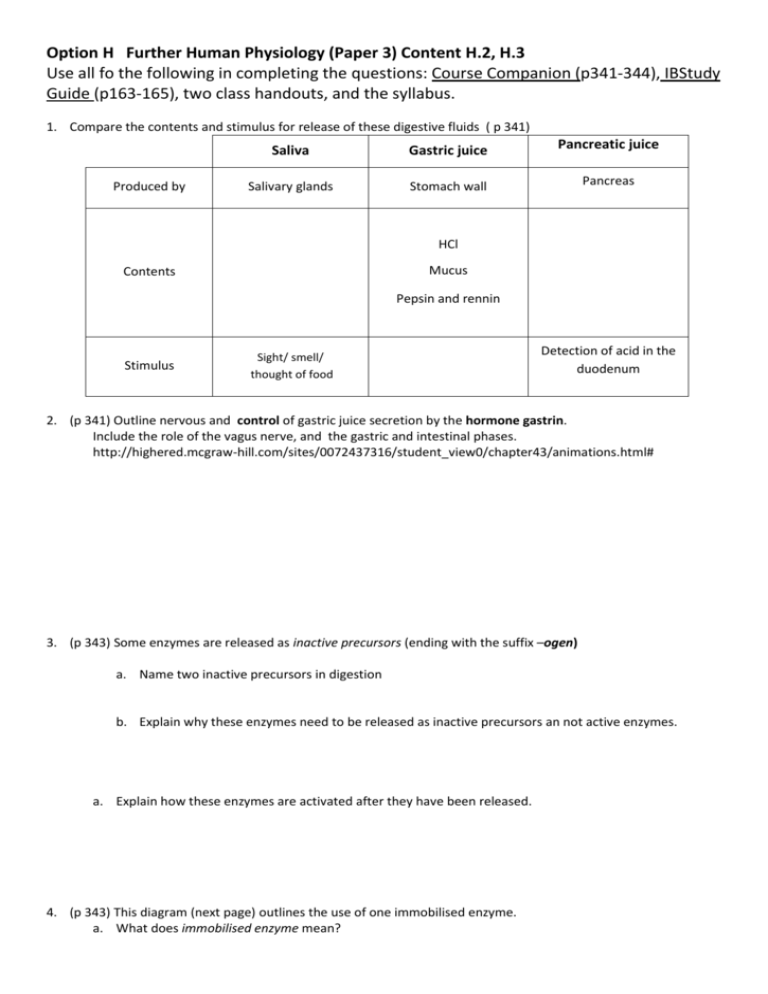
Option H Further Human Physiology (Paper 3) Content H.2, H.3 Use all fo the following in completing the questions: Course Companion (p341-344), IBStudy Guide (p163-165), two class handouts, and the syllabus. 1. Compare the contents and stimulus for release of these digestive fluids ( p 341) Produced by Saliva Gastric juice Pancreatic juice Salivary glands Stomach wall Pancreas HCl Mucus Contents Pepsin and rennin Stimulus Sight/ smell/ thought of food Detection of acid in the duodenum 2. (p 341) Outline nervous and control of gastric juice secretion by the hormone gastrin. Include the role of the vagus nerve, and the gastric and intestinal phases. http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter43/animations.html# 3. (p 343) Some enzymes are released as inactive precursors (ending with the suffix –ogen) a. Name two inactive precursors in digestion b. Explain why these enzymes need to be released as inactive precursors an not active enzymes. a. Explain how these enzymes are activated after they have been released. 4. (p 343) This diagram (next page) outlines the use of one immobilised enzyme. a. What does immobilised enzyme mean? b. Explain how this enzyme is used, including the name of the enzyme and the method of absorption of glucose into the epithelial cells and the blood. c. Why do epithelial cells of the small intestine contain so many mitochondria? d. What are the advantages of using membrane-bound enzymes in digestion of glucose? 5. (p 343) Why can’t cellulose be digested by humans? 6. a. (p 343)What are the difficulties asociated with the digestion of lipids? b. How can the use of bile salts overcome these problems? 7. (p 342) The true cause of stomach ulcers was an important discovery which led to a paradigm shift in medicine and the Nobel prize for the scientists responsible. a. What is a stomach ulcer? b. What was the enduring hypothesis for the cause of stomach ulcers before? http://hopkins-gi.org/mulitmedia/database/Intro_79_H_pylori.swf c. Outline the true cause of most stomach ulcers, including the role of stomach acid and the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. d. What is the most effective treatment for stomach ulcers? 8. (p 344) The ileum is the section of the small intestine responsible for most of the absorption of digested food molecules. a. Draw a transverse section of the ileum. Label and state the functions of: Mucosa, longitudinal and circular muscle, villi, capillaries. b. Label and annotate with functions, these parts of an epithelial cell. State the names of the labeled structures: c. What nutrients are absorbed into the struture labeled ‘2’? 9. (p. 344)Complete the table below to outline how absorption of digested food molecules in the ileum makes use of multiple methods of membrane transport. 10. (p.344) What materials are egested from the alimentary canal?