Ch. 25 B
advertisement

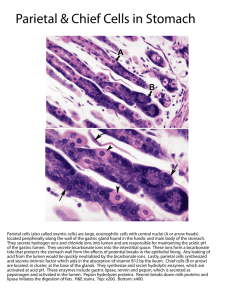
Skeletal muscle deep layer – longitudinal orientation superficial layer – circular orientation superior, middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictors 25-1 Straight muscular tube 25-30 cm long Extends from pharynx to cardiac stomach passing through esophageal hiatus in diaphragm nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium esophageal glands in submucosa skeletal muscle in upper part and smooth in bottom inferior pharyngeal constrictor excludes air from it Lower esophageal sphincter closes orifice to reflux 25-2 25-3 25-4 Series of muscular contractions coordinated by centers in the brain Buccal phase tongue collects food and pushes it back into oropharynx Pharyngeal-esophageal phase soft palate rises and blocks nasopharynx infrahyoid muscles lift larynx; epiglottis folded back pharyngeal constrictors push bolus down esophagus liquids in 2 seconds -- food bolus may take 8 seconds lower esophageal sphincter relaxes 25-5 25-6 Mechanically breaks up food, liquifies food and begins chemical digestion of protein and fat resulting soupy mixture is called chyme Does not absorb significant amount of nutrients absorbs aspirin and some lipid-soluble drugs 25-7 Muscular sac (internal volume from 50ml to 4L) J - shaped organ with lesser and greater curvatures regional differences cardiac region just inside cardiac orifice fundus - domed portion superior to esophageal opening body - main portion of organ pyloric region - narrow inferior end antrum and pyloric canal Pylorus - opening to duodenum thick ring of smooth muscle forms a sphincter 25-8 Cardia Fundus Body Pylorus Notice: bulge of fundus, narrowing of pyloric region, thickness of pyloric sphincter and greater and lesser curvatures 25-9 Innervation by parasympathetic fibers from vagus sympathetic fibers from celiac plexus All blood from stomach enters hepatic portal circulation and is filtered through liver before returning to heart 25-10 25-11 Mucosa simple columnar glandular epithelium lamina propria is filled with tubular glands (gastric pits) Muscularis externa has 3 layers outer longitudinal, middle circular and inner oblique layers 25-12 25-13 Mucous cells Regenerative cells secrete HCl acid and intrinsic factor Chief cells divide rapidly to produce new cells that migrate to surface Parietal cells secrete mucus secrete pepsinogen chymosin and lipase in infancy Enteroendocrine cells G cells Make gastrin Others secrete hormones and paracrine messengers 25-14 25-15 Parietal cells contain carbonic anhydrase (CAH) CO2 + H2O H2CO3 HCO3- + H+ H+ is pumped into stomach lumen by H+K+ATPase HCO3- in blood causes alkaline tide (blood pH ) 2 to 3 L of gastric juice/day (H2O, HCl and pepsin) 25-16 Activates pepsin and lingual lipase Breaks up connective tissues and plant cell walls Converts ingested ferric ions (Fe3+) to ferrous ions (Fe2+) liquefies food to form chyme absorbed and used for hemoglobin synthesis Destroys ingested bacteria and pathogens 25-17 Intrinsic factor Pepsin - protein digestion essential for B12 absorption by small intestine RBC production (lack causes pernicious anemia) secreted as pepsinogen (inactive) HCl converts it to pepsin (active) Gastric lipase and chymosin lipase digests butterfat of milk in infant chymosin curdles milk by coagulating proteins 25-18 25-19 Many produced by enteroendocrine cells hormones enter blood distant cells paracrine secretions neighboring cells Gut-brain peptides signaling molecules produced in digestive tract and CNS 25-20 Swallowing center signals stomach to relax Food stretches stomach activating a receptive-relaxation response resists stretching briefly, but relaxes to hold more food Rhythm of peristalsis controlled by pacemaker cells in longitudinal muscle layer gentle ripple of contraction every 20 seconds churns and mixes food with gastric juice stronger contraction at pyloric region; ejects 3 ml typical meal emptied from stomach in 4 hours 25-21 Induced by excessive stretching of stomach, psychological stimuli or chemical irritants (bacterial toxins) Emetic center in medulla causes retching lower esophageal sphincter to relax stomach and duodenum to contract spasmodically vomiting when abdominal contraction forces upper esophageal sphincter to open 25-22 25-23