Dumas PreLab
advertisement
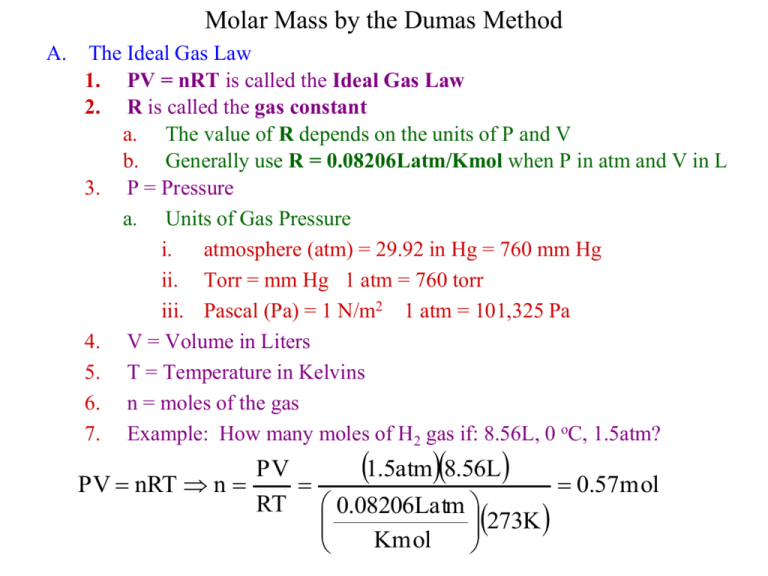
Molar Mass by the Dumas Method A. The Ideal Gas Law 1. PV = nRT is called the Ideal Gas Law 2. R is called the gas constant a. The value of R depends on the units of P and V b. Generally use R = 0.08206Latm/Kmol when P in atm and V in L 3. P = Pressure a. Units of Gas Pressure i. atmosphere (atm) = 29.92 in Hg = 760 mm Hg ii. Torr = mm Hg 1 atm = 760 torr iii. Pascal (Pa) = 1 N/m2 1 atm = 101,325 Pa 4. V = Volume in Liters 5. T = Temperature in Kelvins 6. n = moles of the gas 7. Example: How many moles of H2 gas if: 8.56L, 0 oC, 1.5atm? PV 1.5atm8.56L PV nRT n 0.57mol RT 0.08206Latm 273K Kmol B. The Dumas Method of Determining Molar Mass 1. Modifying the Ideal Gas Law g g gRT PV nRT RT g mol PV mol 2. We will experimentally find g, T, P, V; and we know R: find g/mol 3. Procedure a. Add 5-10 ml of cyclohexane to a 125 ml erlenmeyer flask b. Cover the flask with aluminum foil; poke a small hole in the foil c. Heat the flask in boiling water (400ml beaker) in the hood on hotplate d. When the liquid has just vaporized, cool in an ice bath, dry, weigh e. When finished, fill flask with water and weigh for V (dH2O = 1.00g/ml) C. Safety 1. Cyclohexane and the unknown are flammable-hotplates, not bunsen burner 2. Fumes may be irritating—do the heating in the hood D. How well did you do? 1. Percent Error %Error Exp - 84.2 84.2 2. Repeat the experiment for an unknown x100% Incident: Organic Solvent Fire











