digestive system lecture
advertisement

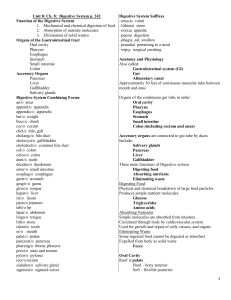
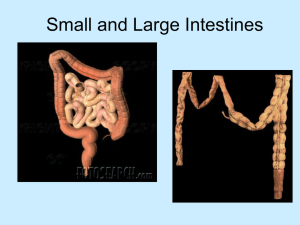
Digestive System Notes • Quiz Friday! 4 main functions: • 1. Ingestion—food material taken into mouth • 2. Digestion—food is broken down, mechanically and chemically, as it travels through the gastrointestinal tract. Digestive enzymes aid the breakdown of complex nutrients. • Proteins → amino acids • Sugars → glucose • Fats → fatty acids or triglycerides 3. Absorption 4. Elimination *The body eliminates • Digested food passes into the bloodstream solid waste materials that through lining cells of cannot be absorbed into bloodstream. the small intestine. • Nutrients travel to all cells of the body. *The large intestine concentrates feces. • Cells burn nutrients to release the energy *The wastes pass out of stored in food. the body through the anus. Small Intestine Villi in the lining of the small intestine help absorb nutrients into the bloodstream. Epiglottis- Flap leading to two tubes. The esophagus & Trachea Diagram on Quiz- No word bank. The Digestive Tract Parts of the Stomach Food travels through the digestive tract by peristalsis (wave like movements) Stomach Continued What is the function of a sphincter? Opens to allow for food to travel through when peristalsis passes by. Parts of the small intestine: Extends from Ilium to anus Function: Major digestive organ. Usable food is prepared for journey into cells of the body. Length? 6-13 feet long 3 parts: D-J-I Duodenum (10 inches) Junum (8 feet) Ileum (12 feet)- joins the large intestines Large Intestines (AKA colon) • Function: Receives fluid waste from digestion and stores until it can be released form the body. • Size? Larger in width then small intestines, but shorter in length (5 feet) • Made up of? Ascending, Transverse & Descending, Sigmoid colon and Anus. • Subdivisions of L.I.? Cecum, appendix, colon, rectum and anal canal. Large Intestines Continued Function of appendix? No real function, not needed! Function Pancreas? Converts food into fuel & helps assist in regulating blood sugar. Function of Gall Bladder? Store & concentrates bile (help in breakdown of fats & food) Functions of the Liver… Besides producing bile, the liver also… • Helps maintain normal blood glucose levels • Manufactures blood proteins necessary for clotting • Releases bilirubin, a pigment in bile • Removes toxins and poisons from the blood Food Pathway through the GI Tract Food enters through the oral cavity and exits through the anus Abnormal Conditions • Hernia – protrusion of an organ or part through the muscle normally containing it Abnormal Conditions Continued • Anal fistula – abnormal tube-like passageway near the anus • Colonic polyposis – polyps (out pouching) protrude from the mucous membrane of the colon • Diverticulosis – abnormal side pockets (outpouchings) in the intestinal wall Abnormal Conditions Continued • Dysentery – painful, inflamed intestines • Hemorrhoids – swollen, twisted, varicose veins in the rectal region • Cirrhosis – chronic degenerative disease of the liver • Viral hepatitis – inflammation of the liver caused by a virus • Cholelithiasis – gallstones in the gallbladder