Digestive Tract
advertisement

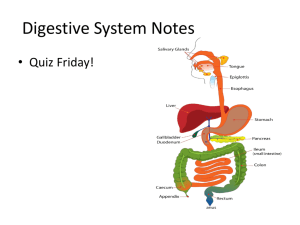
Monday, September 23rd To start, journal your food intake from yesterday. Did you participate in any physical activity? Think Nutritiously Healthy Carbohydrates Glucose, the simplest type of carbohydrate, is the only thing that can be used to meet the energy needs of the body, support the brain and nervous system, and maintain a wellfunctioning digestive system. • Objective: – Identify the parts of the digestive system and their functions. – Explore how food is absorbed in the body. • Vocabulary Words: – – – – – – – – Digestion Absorption Alimentary Canal Saliva Involuntary Reflex Peristalis Chyme Villi Digestion vs. Absorption • Digestion is the process the body uses to break the food into nutrients. – Quick review: What is a nutrient? • Absorption is the process by which nutrients get from the digestive tract into the transportation system that carries them to cells throughout the body. • Food is broken down in the digestive tract or alimentary canal. Digestive Tract • There are seven parts to the digestive tract: – Mouth – Esophagus – Stomach – Small Intestine – Large Intestine – Rectum – Anus Mouth • Sight, smell and taste of food stimulate the flow of a saliva. • Saliva’s job is to soften and moisten food. • Swallowing is an involuntary reflex. Esophagus • The tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. • Muscles contractions called peristalsis carry food along to its next location. Stomach • Churns and breaks down your meal and mixes with gastric juices. • The food now becomes a thin, soupy mixture called chyme. Small Intestine • Digestion ends here. • The tube is almost 6 meters (20 feet) long. • The small intestine is divided into 3 sections: – Duodenum – Jejunum – Illeum Small Intestine • Villi are hairlike projections that increases the surface of the intestinal wall creating more surface area for nutrient absorption. • The food has now been digested. • It will now be absorbed by the blood stream. • Wastes will pass to the large intestine and later be eliminated. Large Intestine • The large intestine has 4 sections: – Ascending colon – goes up – Transverse colon – goes across – Descending colon – goes down – Sigmod Colon – “S” shaped Rectum and Anus • End of the digestive tract. • This is where waste is eliminated. Other Organs – Intestinal Tract • Liver – the processing plan for nutrients • Gallbladder – Bile is stored here • Pancreas – is endocrine and exocrine gland. – It producing several important hormones, including insulin and glucagon. – It secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that pass to the small intestine. – These enzymes help in the further breakdown of the carbohydrates, protein, and fat in the chyme. Nutrition Review What are the seven parts of the digestive tract?