Name: Chapter 14: Human Genetics and Polygenic Traits Test
advertisement

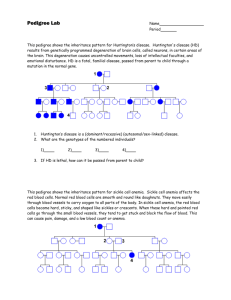
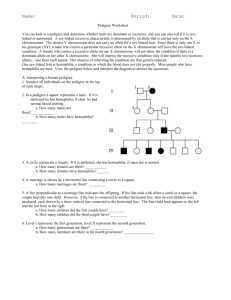
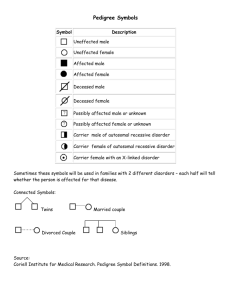
Name:__________________________________________________ Chapter 14: Human Genetics and Polygenic Traits Test Review Sheet 1. Define polygenic – a. Give 3 examples of polygenic traits (phenotypes): b. Give 1 example of a polygenic genotype: 2. What chromosomes determines a male________ 3. What chromosomes determines a female_________ 4. Do a Punnett square below to show how we know that there is a 50% chance of having either a boy or a girl 5. Using the Punnett square above, explain if it is the male or female who is responsible for determining the sex of the offspring. 6. Hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. A person with hemophilia is lacking certain proteins that are necessary for normal blood clotting. Hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele so use “N” for normal and “n” for hemophilia. Since hemophilia is sex-linked, remember a woman will have two alleles (NN or Nn or nn) but a man will have only one allele (N or n). A woman who is heterozygous (a carrier) for hemophilia marries a normal man: a. What are the genotypes of the parents? b. Make a Punnett square for the above cross. c. What is the probability that a male offspring will have hemophilia? __________ d. What is the probability of having a hemophiliac female offspring? _________ 7. Baldness is a sex-linked trait. What parental genotypes could produce a bald woman? *use H =normal hair, and h = bald 8. If cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disease and Gary has the disorder but neither of his parents does, what are the chances that one of Gary’s brother’s will also have the disorder? 9. Marfan’s syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder that causes elongation of the limb and finger bones. John, who was recently diagnosed with Marfan’s syndrome, has a mother with the disorder but a father who does not. If John married Jen who is normal what are the chances they will have a child with Marfan’s syndrome? 10. The following pedigree shows the transmission of a rare, but not fatal, genetic disorder in a family. A. A. Identify the mode of inheritance suggested by the pedigree; X-linked, auto dom or auto rec. B. B. Indicate the genotypes of all the individuals in the pedigree above, by writing the genotype below the individual in the chart. 11. In the following pedigrees, state by answering yes or no in the appropriate blank space, whether transmission of the trait could be accounted for on the basis of each of the listed simple modes of inheritance. Pedigree A Pedigree B Autosomal recessive __________ __________ Autosomal dominant __________ __________ X-linked recessive __________ __________