Life Science Second Semester Study Guide
advertisement

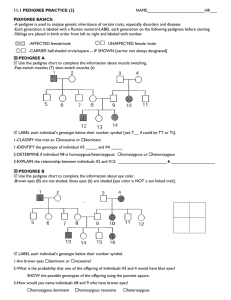
Life Science Second Semester Study Guide The final will have 2 parts: multiple choice and short answer including genetic problem solving. The questions will be from chapter 5, 6, 7, parts of 8 which were included with chapter 7 notes, kingdoms notes, & the human body system notes. You are responsible for all of them in detail. Make sure to study all key terms, notes, and workbook. Also do not forget to read the book! Some Important Ideas: 1. Explain Mendel’s genetics experiments. 2. Identify the factors that control the inheritance of traits in organisms. 3. Explain how geneticists use symbols to represent alleles. 4. How are Punnett Squares useful to geneticists? 5. Use Punnett Square to cross single genes & codominance. a. In Mountain Boomers, the gene for long tail is dominant over the gene for short tail. Use a Punnett Square to predict the result of a cross between a homozygous Long-tailed and a homozygous Shorttailed Mountain Boomer. What do the offspring look like? b. In dogs, wire-hair (W) is dominant to smooth (w). In a cross of a homozygous wire-haired dog with a smooth-haired dog… i. What will be the phenotype of the F1 generation? ii. What would be the genotypes? iii. What would be the ratio of wire-haired to smooth-haired dogs in the F2 generation produced from the F1? c. Red-green colorblindness is inherited as a sex-linked recessive gene and is found only on the X chromosome. A person with this affliction cannot distinguish between shades of red and green due to a lack of a special protein in the color receptors of the eye. A man with normal vision marries a woman who is red-green color blind. What are their genotypes? What is the probability that their children will be colorblind? d. A person with blood type B marries a person with blood type AB. i. What are the possible genotypes for these 2 people? ii. If these parents have a child with blood type A, what is their exact genotype? iii. Draw the Punnett Square and write the genotypic and phenotypic ratios to find out the chances of having a child with type A blood. iv. What kind of inheritance is this? 6. Describe the role of chromosomes in inheritance. 7. Identify and describe the events that occur in meiosis. What types of cells form by meiosis? 8. What is meant by the term “genetic code”? 9. Describe the process by which a cell produces protein. 10. Describe different types of mutations and how they affect an organism. 11. Explain why some traits show a large variety of phenotypes. 12. Explain how environmental factors can alter the effects of gene. 13. Why are some sex-linked traits more common in males than in females? 14. What are two major causes of genetic disorders in humans? 15. Describe the causes and symptoms of four human genetic disorders. 16. How are genetic disorders diagnosed? 17. Describe three ways in which people have developed organisms with desired traits. 18. Explain how DNA fingerprinting is used. 19. State the goal of the Human Genome project. 20. Review lessons 7-1, 7-2, 7-3 21. Why is scientific naming important? How do you make a scientific name? 22. What are the major levels of classifications? Know the classification system of humans. 23. How does a branching tree diagram show evolutionary relationships? 24. What methods do geologists use to determine the absolute age of a rock? 25. What must scientists do first to date a rock radioactively? Second? 26. Is an index fossil used to determine absolute age or relative age? Explain. (p.276) 27. Study the 6 kingdoms of life notes. 28. Study the human system notes. 29. Know how to interpret a pedigree. Interpreting a Human Pedigree Use the above figure to answer the questions below. 1. Number all individuals on the pedigree at the top of each shape. 2. In a pedigree, a square represents a male. If it is darkened he has hemophilia; if clear, he had normal blood clotting. a. How many males are there? __________________ b. How many males have hemophilia? ____________ 3. A circle represents a female. If it is darkened, she has hemophilia; if open she is normal. a. How many female are there? _________________ b. How many females have hemophilia? __________ 4. A marriage is indicated by a horizontal line connecting a circle to a square. a. How many marriages are there? _______________ 5. A line perpendicular to a marriage line indicates the offspring. If the line ends with either a circle or a square, the couple had only one child. However, if the line is connected to another horizontal line, then several children were produced, each indicated by a short vertical line connected to the horizontal line. The first child born appears to the left and the last born to the right. a. How many children did the first couple (couple in row I) have? ______________ b. How many children did the third couple (couple in row III) have? _____________ 6. Level I represent the first generation; level II represents the second generation. a. How many generations are there? _______________ b. How many members are there in the fourth generation? _____________