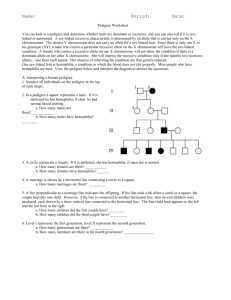
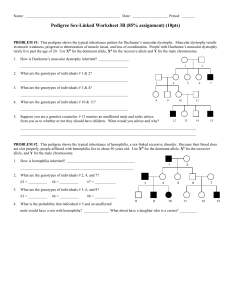
Why can bacteria and viruses read human genes
advertisement
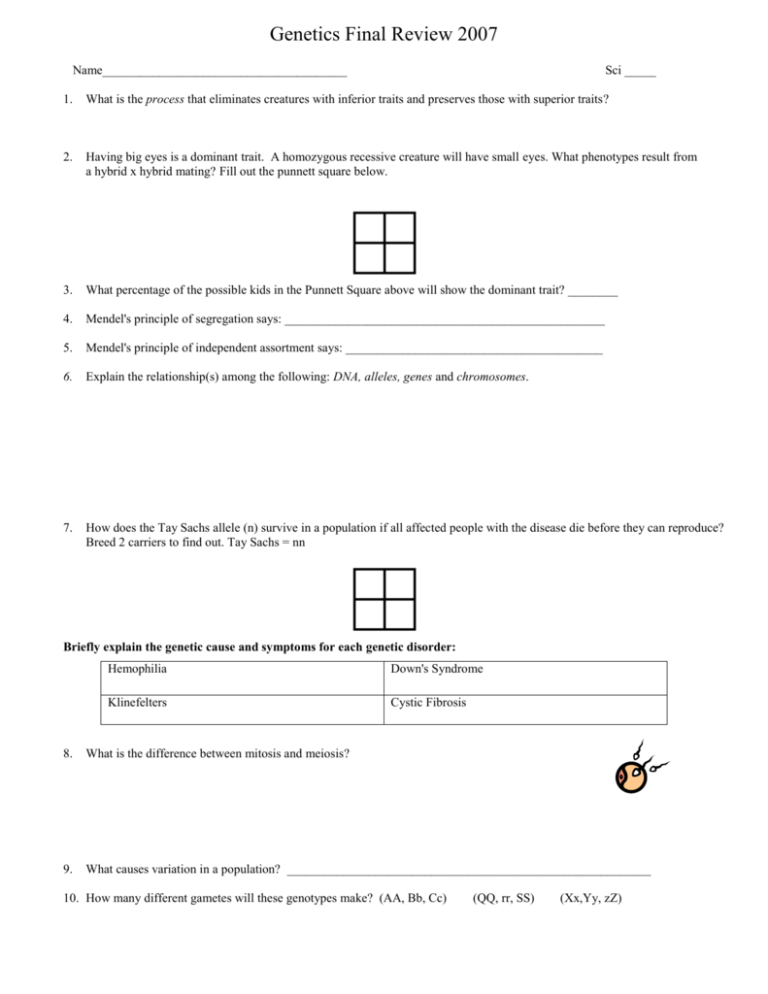
Genetics Final Review 2007 Name_______________________________________ Sci _____ 1. What is the process that eliminates creatures with inferior traits and preserves those with superior traits? 2. Having big eyes is a dominant trait. A homozygous recessive creature will have small eyes. What phenotypes result from a hybrid x hybrid mating? Fill out the punnett square below. 3. What percentage of the possible kids in the Punnett Square above will show the dominant trait? ________ 4. Mendel's principle of segregation says: ___________________________________________________ 5. Mendel's principle of independent assortment says: _________________________________________ 6. Explain the relationship(s) among the following: DNA, alleles, genes and chromosomes. 7. How does the Tay Sachs allele (n) survive in a population if all affected people with the disease die before they can reproduce? Breed 2 carriers to find out. Tay Sachs = nn Briefly explain the genetic cause and symptoms for each genetic disorder: Hemophilia Down's Syndrome Klinefelters Cystic Fibrosis 8. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? 9. What causes variation in a population? __________________________________________________________ 10. How many different gametes will these genotypes make? (AA, Bb, Cc) (QQ, rr, SS) (Xx,Yy, zZ) Genetics Final Review 2007 11. Draw the offspring in punnett squares when (Bb, ee) mates with (bb, eE). Draw a round head for each creature. Key: B = Big Nose, bb = no nose E = 2 eyes, ee = one eye 12. Recessive sex-linked conditions like hemophilia and colorblindness are most common in boys because…. 13. A woman is a carrier of hemophilia (XN Xn) and she marries a healthy male (XN Y). Hemophilia is represented by “n”. A normal, healthy allele = “N”. Draw a punnett square and predict their kids. 14. _______ % What percentage of the offspring in the problem above will have hemophilia? 15. Which part of the cell manufactures new protein? ________________________________________________________ 16. Who is responsible for producing sons with hemophilia? MOM 17. DAD Is the following recessive disease sex-linked or autosomal? Look at the pedigree below. Write the genotype of each parent to find out. Let “N” represent a normal allele and “n” represent an abnormal allele. A shaded shape represents a person who has a genetic disease. Square = male, circle = female. (Autosomal chromosomes are not sex chromosomes.) 18. What are the genotypes of both parents? The following pedigree shows a recessive, sex-linked disease. The affected son has the following genotype: XnY. 19. Population Genetics: The frequency of the sickle cell allele (n) in a population is 0.3. What percent of the population will be carriers? N= n = 0.3 N n 20. What ratios result from a dihybrid x dihybrid mating? (Aa, Bb) x (Aa, Bb)