Microscopes and Cells
advertisement

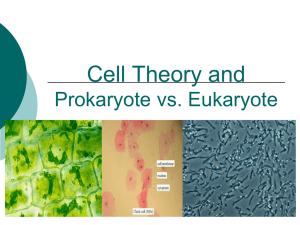
The History of the Cell How did we discover cells? –Discovery made possible by the invention of the microscope –Mikros = small –Skopein = look Microscopes and Cells 1600’s. –Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living cells as seen through a simple microscope. Microscopes and Cells –Robert Hooke used the first compound microscope to view thinly sliced cork cells. •Compound scopes use a series of lenses to magnify in steps. •Hooke was the first to use the term “cell”. Robert Hooke's Drawing of Cork Cells Actual cork cells Microscopes and Cells 1830’s. –Mathias Schleiden identified the first plant cells and concluded that all plants were made of cells. - Theodore Schwann made the same conclusion about animal cells. Plant and Animal Cells Cell Theory: All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life All cells come from preexisting cells. All Cells Cells do have some basic structures in common 1) Cell membrane 2) DNA 3) Ribosomes 4) Cytoplasm All cells have a membrane cell membrane = plasma membrane Function – controls what enters and exits the cell, helps to maintain cell homeostasis NOT the same as cell wall (only some cells) (more coming in ch. 8) All cells have DNA code DNA is a nucleic acid What is the purpose of DNA (and nucleic acids in general)? Again, more details coming later in genetics unit (ch. 13) All cells have ribosomes They look like tiny dots in overall cell If DNA has protein code, ribosomes build the protein according to the code All cells have ribosomes Ribosome sliding along a nucleic acid, reading its code to assemble amino acids together into a protein Two Basic Cell Types 1) Prokaryotic Cells: – Lack internal compartments (organelles) – No true nucleus. – All are single-celled (unicellular) organisms. – Examples: bacteria – Smaller, simpler cells than eukaryotes Two Basic Cell Types 2) Eukaryotic Cells – Have several internal structures (organelles). – True nucleus. – Either unicellular or multicellular. – plants and animals, fungi, protists – Much more complex and larger then prokaryotic cells Simple to complex… Prokaryotic cells are simple Eukaryotic cells are complex Can you guess which type may have evolved from which type? Eukaryotic from Prokaryotic Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Now compare the two groups side by side: Prokaryotes No definite nucleus No membrane bound organelles All are bacteria! Unicellular Eukaryotes Have a defined nucleus have membrane-bound organelles plants, animals, protists, or fungi May be single or multi-cellular Now think of what Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common and use them to complete the following bubble map. Remember the characteristics of all living things!! Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Ask if you have a different answer. DNA No organelles organelles cytoplasm Unicellular Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Defined Nucleus Cell membrane Multi or Unicellular No nucleus Ribosomes