Apr 25th
advertisement

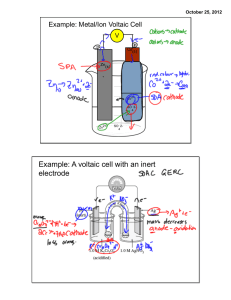
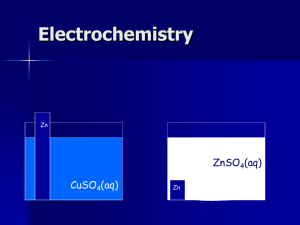
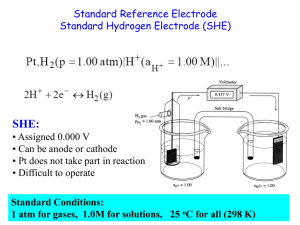
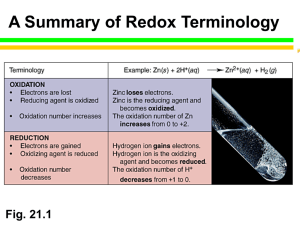
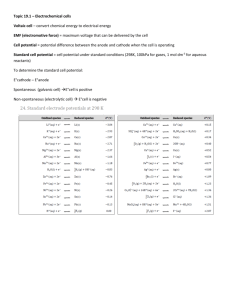
SI Chem 178 Ch 20 Leader: Emily April 25, 2013 (Thurs) Quiz on Friday – work individually, 20 minutes 1. determine spontaneous redox reaction given standard reduction potentials and write the associated balanced redox equation. 2. calculate standard cell potential Eo and Go given the equilibrium constant K. Relate to spontaneity of reaction. 3. Identify/rank strengths of oxidizing and/or reducing agents given standard reduction potentials. Recommended problems for recitation & quiz on Friday: Chapter 20: 4 - 8, 30, 32, 35, 38d, 39, 41, 43bc, 44bd, 45, 47, 52b, 53, 55c, 58, 61, 63, 68, 69, 74, 75, 77 Review: 20.4 You want to make a voltaic cell using the following half reactions: A2+(aq) + 2e- A(s) Ered =-0.10 V B2+(aq) + 2e- B(s) Ered =-1.10 V -Draw out a generalized voltaic cell – what all do you need? -Which is the cathode, anode? Which direction will e- move? -What is your calculated Ecell? Complete and balance the following rxn: BrO3-(aq) + N2H4(g) Br-(aq) + N2(g) Acidic Solution New Stuff: If E is +, G is ____________ and the reaction is ______________________ A higher / lower Ered shows preference to be reduced. Ecell = _________________ - ____________________ In a concentration cell, you have the same / different electrodes. When concentrations are equal in a concentration cell, the voltmeter will read _________ What is the form of the Nernst equation that we use for concentration cells? 20.43 Which is the stronger reducing agent: Ca(s) or Al(s) 20.44 Which is the stronger oxidizing agent: Zn2+ or Cd2+ 20.46 Classify each of the following as being more likely to serve as an oxidant or reductant: Ce3+(aq) Ca(s) ClO3-(aq) N2O5(g) 20.53 In a given reaction, the equilibrium constant (K) is 1.5*10^-4 at 298K, calculate G* and E*red. Also try problem #58 20.69 Concentration Cell: Two Zn electrodes with Zn2+ solutions Solution 1 at 1.8M and Solution 2 at 0.01M Which is the cathode, anode (where will Zn2+ increase/decrease)? What is the std EMF? What is the cell EMF?