Bryophyta
advertisement

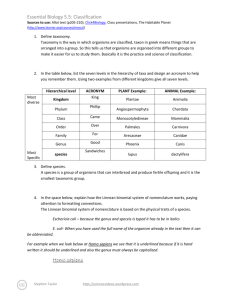
PLANT PHYLA COMPARISONS Plant Phyla Bryophyta Filicinophyta Coniferophyta Angiospermophyta Various terms Rhizoids but no true Vegetative organs-parts of the plant concerned roots. Some with simple with growth rather than stems & leaves; others reproduction have only a thallus Vascular tissue- tissues with tubular structures used for transport within the plant Cambium- cells between xylem and phloem that can produce more of these tissues Pollen- small structures containing male gametes that are dispersed Ovules- contains a female gamete & develops into a seed after fertilization Seeds-dispersible unit consisting of an embryo plant and food reserves, inside a seed coat Fruits- seeds together with a fruit wall developed from the ovary wall Roots, stems, & leaves are usually present No xylem or phloem Xylem and Phloem are both present No cambium, no true trees & shrubs Present in conifers & most angiosperms, allowing secondary thickening of stems & roots & development of plants into trees & shrubs Pollen is not produced Pollen is produced Pollen is produced by in male cones anthers in flowers No ovaries or ovules No seeds Ovules are produced in female cones Ovules are enclosed inside ovaries in flowers Seeds are produced and dispersed No fruits Fruits produced for dispersal of seeds Bryophyta LIVERWORT MOSS HORNWORT Filicinophyta FERNS Coniferophyta CONIFERS Angiospermophyta FLOWERING PLANTS Phylum & Examples Mouth/Anus Symmetry Porifera No mouth or anus None Cnidaria Mouth only Radial Platyhelminthes Mouth only Bilateral Mollusca Mouth and anus Bilateral Annelida Mouth and anus Bilateral Mouth and anus Bilateral Arthropoda Skeleton Other External Recognition Features Many pores over the surface Internal spicules (skeletal needles) through which water is drawn in for filter feeding. Varied shapes Soft, but hard corals Tentacles arranged in rings around the mouth, with secrete CaCO3 stinging cells. Polyps or medusae (jellyfish) Flat & thin bodies in the shape of a ribbon. No blood system or system for gas exchange Most have shell made A fold in the body wall called the mantle secretes the shall. of CaCO3 A hard rasping radula is used for feeding. Soft with no skeleton Internal cavity with Bodies made up of many ringfluid under pressure shaped segments, often with External skeleton made of plates of chitin bristles. Blood vessels often visible Segmented bodies and legs or other appendages with joints between the sections. Porifera SPONGES Cnidaria Hydra Sea anemone Jellyfish Coral Platyhelminthes Tapeworms Flatworms Flukes Mollusca Snails Octopus Bivalves Squids Gastropods Annelida Oligochaetes Marine Bristleworms Leeches Arthropoda Insects Crustaceans Arachnids Myriapods