IB Biology Topic 5.5
advertisement
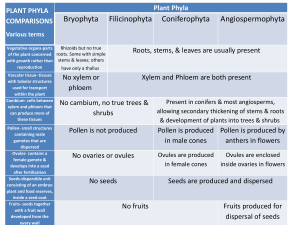
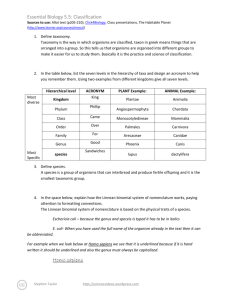
IB BIOLOGY TOPIC 5.5 CLASSIFICATION TOPICS: 5.5.1 Outline the binomial system of nomenclature 5.5.2 List seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa using an example from two different kingdoms for each level. 5.5.3 Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using simple external recognition features: bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and angiospermophyta. 5.5.4 Distinguish between the following phyla of animals, using simple external recognition features: porifera, cnidaria, platyhelminthes, annelida, mollusca and arthropoda. 5.5.5 Apply and design a key for a group of up to eight organisms. 5.5.1 OUTLINE THE BINOMIAL SYSTEM OF NOMENCLATURE Species are a group of organisms with similar characteristics which can interbreed and produce fertile offspring whereas a genus is a group of similar species. Species need an international name and so biologists name them using the binomial system of nomenclature. Each species is given two names. The first is the genus name and is given an upper case first letter. I.E. Homo The second is the species name and is given a lower case first letter. I.E. sapiens Homo sapien is the correct binomial nomenclature for humans. 5.5.2 LIST SEVEN LEVELS IN THE HIERARCHY OF TAXA USING AN EXAMPLE FROM TWO DIFFERENT KINGDOMS FOR EACH LEVEL. Red Kangaroo: Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Diprotodontia Family: Macropodidae Genus: Macropus Species: rufus White Oak tree: Kingdom: Plantae Phylum: Magnoliophyta Class: Magnoliopsida Order: Fagales Family: Fagaceae Genus: Quercus Species: alba 5.5.3 5.5.4 • • • • • • • • • • Porifera: no clear symmetry attached to a surface pores through body no mouth or anus example: sponges Cnidaria: radially symmetric tentacles stinging cells mouth but no anus example: jellyfish • • • • • • • • • • Platyhelminths: bilaterally symmetrical flat bodies unsegmented mouth but no anus example: tapeworm Annelida: bilaterally symmetrical bristles often present segmented mouth and anus example: earthworm • • • • • • • • • • Mollusca: muscular foot and mantle shell may be present segmentation not visible mouth and anus example: slugs and snails Arthropoda: bilaterally symmetric exoskeleton segmented jointed appendages example: spiders and insects