05.5 Classification worksheet
advertisement

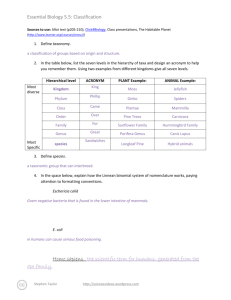
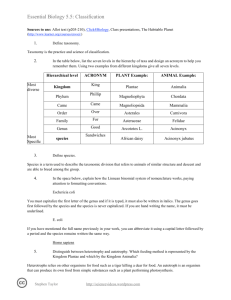
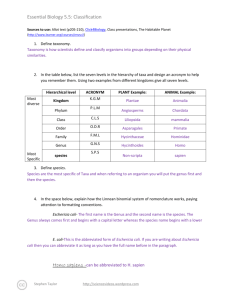
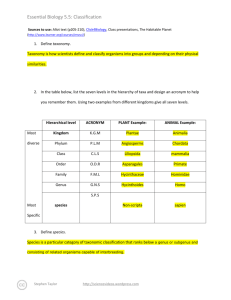
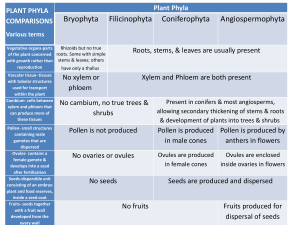
Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Sources to use: Allot text (p205-210), Click4Biology, Class presentations, The Habitable Planet (http://www.learner.org/courses/envsci/) 1. Define taxonomy. Taxonomy is the way in which organisms are classified, taxon in greek means things that are arranged into a group. So this tells us that organisms are organized into different groups to make it easier for us to study them. Basically it is the practice and science of classification. 2. In the table below, list the seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa and design an acronym to help you remember them. Using two examples from different kingdoms give all seven levels. Hierarchical level Most diverse ACRONYM King Kingdom Phillip Phylum Most Specific PLANT Example: ANIMAL Example: Plantae Animalia Angiospermophyta Chordata Class Came Monocotyledineae Mammalia Order Over Palmales Carnivora Family For Arecaceae Canidae Genus Good Phoenix Canis lupus dactylifera Sandwiches species 3. Define species. A species is a group of organisms that can interbread and produce fertile offspring and it is the smallest taxonomic group. 4. In the space below, explain how the Linnean binomial system of nomenclature works, paying attention to formatting conventions. The Linnean binomial system of nomenclature is based on the physical traits of a species. Eschericia coli – because the genus and speceis is typed it has to be in italics E. coli- When you have used the full name of the organism already in the text then it can be abbreviated. For example when we look below at Homo sapiens we see that it is underlined because if it is hand written it should be underlined and also the genus must always be capitalized. Homo sapiens Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 5. Distinguish between heterotrophy and autotrophy. Which feeding method is represented by the Kingdom Plantae and which by the Kingdom Animalia? Heterotrophy and autotrophy are two methods of feeding, heterotrophs are organisms that reply on killing other animals for food because they do not produce their own food and autotrophs are organisms that do not reply on other resources for food because they make their own this is represented in Kingdom Plantae and heterotrophs are represented in Kingdom Animalia. 6. Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using external characteristics. Give examples. It is very simple, with no roots or stem, with small leaves and a fury appearance. It has roots, short stems and leaves, the leaves are divided up into sections and may sometimes be curled. Have pine needles for leaves and is a woody tree It has roots, stems and leaves and it produces flowers 50cm 15m Spores released from capsule at end of the stalk Spores are produced in sporangia and there are capsules under the leaves 100m The seeds develop in female cones 100m The seeds dispersed through fruits 7. Have a go at using a dichotomous key here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/animals.html Take the opportunity to build your vocabulary while completing this task. Think of an animal, answer the questions and work through the classification. Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 8. Distinguish between the following phyla of animals, using external recognition features and giving examples. Check your answers here: http://www.scenicoregon.com/webanic/pages/map.html ` No mouth or anus none Porous, attached to rocks, filter feed radial Mouth, no anus none Tentacle around mouth, stinging cells bilateral Mouth, no anus none Ribbon shaped body, commonly parasites bilateral Mouth and anus Very segmented May have bristles and visible blood vessels Bilateral foot, shell not Mouth and anus Not visible Many have shell, uses sharp radula for rasping on food bilateral Mouth and anus Segmented, may have joints none 9. Distinguish between these terms: Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Exoskeleton, jointed appendages Essential Biology 5.5: Classification Radial symmetry vs Bilateral symmetry vs Asymmetrical Radial symmetry is when no matter what angle you look at the organism from it is going to be symmetrical. Bilateral symmetry is when the organism is symmetrical from one point generally directly through the middle. Asymmetrical symmetry is when there is no symmetry and the organism just completes itself on the opposite side not symmetrically. 10. Design and apply a dichotomous key to distinguish between these Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.5: Classification 11. Queensland shark species: 12. Look at the species names for the sharks in the chart. a. Which of the following pairs is most closely related? A. Black Tip Reef Shark and White Shark B. Grey Reef Shark and Shortfin Mako C. Grey Reef Shark and Winghead D. Creek Whaler and Black Tip Reef Shark b. Explain your answer to a. I think the Creek Whaler and the Black Tip Reef Shark are more closely related then the other three options I was given because they have the same genus compared to the others that did not have the same genus. c. Which of the following is/are true for the Great Hammerhead and Scalloped Hammerhead? i. They are two subspecies of the same species A. B. C. D. ii. They are two species in the same genus iii. They are members of the same order iv. They are from different phyla i only i and ii ii and iii iv only d. Which of the following is/are true of all of the sharks in the chart? i. They are members of the same species ii. They are part of the same genus iii. They are part of the same class iv. They are part of the same kingdom B. i only C. i and ii D. ii and iii E. iii and iv Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com