ORAL HYPOGLYCAEMIC DRUGS
advertisement

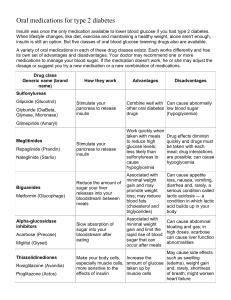
Oral hypoglycemic drugs Prof. Hanan Hagar Objectives By the end of this lecture, students should be able to: 1. Classify different categories of oral hypoglycemic drugs. 2. Identify mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of each class of oral hypoglycemic drugs. 3. Identify the clinical uses of hypoglycemic drugs 4. Know the side effects, contraindications of each class of oral hypoglycemic drugs. Oral hypoglycemic drugs 1. Sulfonylurea drugs 2. Meglitinides 3. Biguanides 4. alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. 5. Thiazolidinediones. 6. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors Oral hypoglycemic drugs Insulin secretagogues Sulfonylurea drugs Meglitinides Insulin sensitizers Biguanides Thiazolidinediones Others Alpha glucosidase inhibitors Gastrointestinal hormones Insulin secretagogues Are drugs which increase the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas Include: • Sulfonylureas • Meglitinides Mechanism of action of sulfonylureas: Stimulate insulin release from functioning B cells by blocking ATP-sensitive K+ channels which causes depolarization and opening of voltage- dependent Ca 2+ channels, which causes an increase in intracellular calcium in the beta cells and stimulates insulin release. Mechanism of action of sulfonylureas: Glucose Sulfonylureas Meglitinides Blockade of ATPsensitive K channels depolarization and opening of voltage- dependent calcium channels Exocytosis & insulin release ↑ in intracellular calcium in the beta cells Mechanisms of Insulin Release Classification of sulfonylureas First generation Short acting Tolbutamide Intermediate acting Acetohexamide second generation Long acting Chlorpropamide Short acting Long acting Glipizide Tolazamide Glibenclamide (Glyburide) Glimepiride Pharmacokinetics of sulfonylureas: Orally, well absorbed. Reach peak concentration after 2-4 hr. All are highly bound to plasma proteins. Duration of action is variable. Second generation has longer duration than first generation. Pharmacokinetics of sulfonylureas: Metabolized in liver excreted in urine (elderly and renal disease) Cross placenta, stimulate fetal β-cells to release insulin → fetal hypoglycemia First generation sulfonylureas Tolbutamide Acetohexamide Tolazamide short-acting intermediate- intermediate -acting acting Chlorpropa mide longacting Absorption Well Well Slow Well Metabolism Yes Yes Yes Yes Metabolites Inactive Active Active Inactive Half-life 4 - 5 hrs 6 – 8 hrs 7 hrs 24 – 40 hrs Short (6 – 8 hrs) Intermediate (12 – 20 hrs) Intermediate (12 – 18 hrs) Long ( 20 – 60 hrs) Urine Urine Urine Urine Duration of action Excretion First generation sulfonylureas Tolbutamide: safe for old diabetic patients or patients with renal impairment. Second generation sulfonylureas Glipizide - glyburide (Glibenclamide) More potent than first generation Have longer duration of action. Less frequency of administration Have fewer adverse effects Have fewer drug interactions Second generation sulfonylureas Glipizide Glibenclamide (Glyburide) Glimepiride Absorption Well Well Well Metabolism Yes Yes Yes Metabolites Inactive Inactive Inactive Half-life 2 – 4 hrs Less than 3 hrs 5 - 9 hrs 10 – 16 hrs 12 – 24 hrs 12 – 24 hrs short long long Divided doses 30 min before meals Single dose Single dose Urine Urine Urine Duration of action Doses Excretion Unwanted Effects: Hyperinsulinemia & Hypoglycemia: Less in tolbutamide. More in old age, hepatic or renal diseases. Weight gain due to increase in appetite GIT upset. Allergic reactions in pts sensitive to sulfa drugs CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hepatic impairment or renal insufficiency Pregnancy & lactation Meglitinides e.g. Repaglinide are rapidly acting insulin secretagogues Mechanism of Action: Stimulate insulin release from functioning β cells via blocking ATP-sensitive K-channels resulting in calcium influx and insulin exocytosis. Pharmacokinetics of meglitinides Orally, well absorbed. Very fast onset of action, peak 1 h. short duration of action (4 h). Metabolized in liver and excreted in bile. Taken just before each meal (3 times/day). Uses of Meglitinides Type II diabetes Specific use in patients allergic to sulfur containing drugs e.g. sulfonylureas. Can be used as monotherapy or combined with metformin Adverse effects of Meglitinides Hypoglycemia. Weight gain. Insulin sensitizers Are drugs which increase the sensitivity of target organs to insulin. Include Biguanides Thiazolidinediones (Glitazones) Insulin sensitizers Biguanides e.g. Metformin Does not require functioning B cells. Does not stimulate insulin release. Mechanism of action of metformin Decrease insulin resistance. Increases peripheral glucose utilization (tissue glycolysis). Inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis. Impairs glucose absorption from GIT. LDL , VLDL & HDL Pharmacokinetics of metformin orally. Not bound to serum protein. Not metabolized. t ½ 3 hours. Excreted unchanged in urine Uses of metformin Type II diabetes particularly in overweight and obese people (with insulin resistance). Advantages: No risk of hypoglycemia Mild weight loss (anorexia). Adverse effects of metformin GIT disturbances: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Long term use interferes with vitamin B12 absorption. Lactic acidosis: in patients with renal, liver, pulmonary or cardiac diseases. Metallic taste in the mouth. Contraindications of metformin Pregnancy. Renal disease. Liver disease. Alcoholism. Conditions predisposing to hypoxia as cardiopulmonary dysfunction. Insulin sensitizers Thiazolidinediones (glitazones) Pioglitazone (Actos) Mechanism of action – – – – Activate PPAR- (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor -). Decrease insulin resistance. Increase sensitivity of target tissues to insulin. Increase glucose uptake and utilization in muscle and adipose tissue. Pharmacokinetics of pioglitazone – Orally (once daily dose) – Highly bound to plasma albumins (99%) – Slow onset of activity – Half life 3-4 h – Metabolized in liver – Excreted in urine 64% & bile Uses of pioglitazone Type II diabetes with insulin resistance. Used either alone or combined with sulfonylureas, biguanides. No risk of hypoglycemia when used alone. Adverse effects of pioglitazone Hepatotoxicity ?? (liver function tests for 1st year of therapy). Fluid retention (Edema). Precipitate congestive heart failure Mild weight gain. Contraindications of pioglitazone Congestive heart failure. Pregnancy. Lactating women Significant liver disease. -Glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose -Glucosidase inhibitors Are reversible inhibitors of intestinal glucosidases in intestinal brush border that are responsible for carbohydrate digestion. decrease carbohydrate digestion and glucose absorption in small intestine. -Glucosidase inhibitors Decrease postprandial hyperglycemia. Taken just before meals. No hypoglycemia if used alone. Kinetics of -glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose Given orally, poorly absorbed. Metabolized by intestinal bacteria. Excreted in stool and urine. Uses of -glucosidase inhibitors Effective alone in the earliest stages of impaired glucose tolerance. Can be combined with sulfonylurea in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes to improve blood glucose control. Adverse effects of -glucosidase inhibitors GIT: Flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal pain Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors DPP- 4 inhibitors e.g. Sitagliptin (DPP- 4 inhibitors) Sitagliptin Orally Given once daily half life 8-14 h Dose is reduced in pts with renal impairment Mechanism of action of sitagliptin Sitagliptin inhibits DPP-4 enzyme, which metabolizes the naturally occurring incretin hormones thus increase incretin secretion (gastrointestinal hormones secreted in response to food). Incretin hormones decreases blood glucose level by : Increasing insulin secretion Decreasing glucagon secretion. mechanism of action of Sitagliptin Clinical uses Type II diabetes mellitus as a monotherapy or in combination with other oral antidiabetic drugs when diet and exercise are not enough. Adverse effects Nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea. SUMMARY Class Mechanism Sulfonylureas Tolbutamide Glipizide Glibenclamide (glyburide) Stimulating insulin production by inhibiting the KATP channel Meglitinides repaglinide Stimulates insulin secretion Site of action Main advantages Pancreatic beta cells • Effective • Inexpensive Pancreatic beta cells Sulfa free Biguanides Metformin Decreases insulin resistance Liver Thiazolidinedio nes pioglitazone Decreases insulin resistance Fat, muscle -Glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose Inhibits αglucosidase GI tract DPP-4 inhibitor Sitagliptin Increase secretin GI tract Main side effects • Hypoglycemia • Weight gain • Allergy •Hypoglycemia •Weight gain • mild • GIT symptoms, weight loss • Lactic acidosis • No hypoglycemia • Metallic taste Hepatoxicity Edema Low risk •GI symptoms, flatulence