ANCIENT GREECE

ANCIENT
GREECE
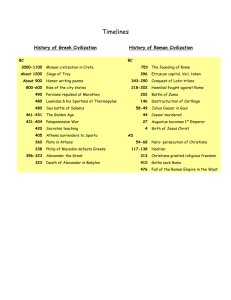
1900-133 BCE
Agenda
• Bellringer (10 min)
• Circle Map (10 min)
• Notes (30 min)
• Letter (20 min)
• Fall of Rome Video and
Questions (15 min)
• Project (5 min)
• Everyday Bellringer
Question
• Explain how the artifact you created/photographed/found is representative of one of the civilizations we studied yesterday.
Greece and
Rome
SPRITE
Social
Political
Religious
International
Technology
Economics
Teacher Choice:
As you go through the powerpoint, have the students fill out charts for
Greece and Rome. You may also take
Cornell Notes.
Greece GEOGRAPHY
• Mountain Ranges – protection & isolation
• Seas – trade & expansion
• Peninsulas – protection & trade
• Islands – trade & expansion
ATHENS
• Early Athens was ruled by a king and later by an oligarchy.
• After a series of bad rulers, Athenians would unite and create a democracy.
• Democracy is governed by the people or rule of the many.
SPARTA
• ***Sparta was a military state governed by an oligarchy, rule by the few.***
• Spartan men were bred to be warriors and nothing else.
RELIGION
• The Greeks were polytheistic.
• In Greece, Gods were seen as unpredictable, cruel, and powerful.
PHILOSOPHY
• Philosophy is an organized system of thought or “love of wisdom.”
SOCRATES
• Socrates – Believed that the only goal in education was to improve the individual.
• He used the Socratic method, question and answer, to teach.
• “The unexamined life is not worth living.”
PLATO
• He believed that society should be divided into three basic groups: an upper class of philosophers and kings, a second group of warriors, and a third group containing the rest.
ARISTOTLE
• Aristotle analyzed 158 states and their governments and concluded that only three forms of government were truly effective: Monarchy,
Aristocracy, Constitutional
Government.
ALEXANDER THE GREAT
• Macedonian King 356-323
BCE.
• Only 20 years old when he became king.
ALEXANDER’S LEGACY
• Alexander took Syria,
Palestine, and Egypt, and the Persian Empire.
• ***Alexander’s conquests led to the Hellenistic Era where Greek language, architecture, literature, and art spread throughout the world.***
Important Contributions from Greece
• Art
• Democracy
• Drama
• Philosophy
• Literature
• The Olympics
ALEXANDER’S EMPIRE
Ancient Rome
The Geography of Rome-
Geography is Destiny
• Rome’s power grew due to its geography.
• Close to the sea and in the middle of
Europe, it became the epicenter of Europe.
The Roman Builders- All over the
Empire
• Roads that still last
• Aqueducts- bringing water to every important city
• Forum- public area of the city- center- oration etc.
• Theaters- for entertainment- drama
• Coliseums- more fun, fights, gladiators, animals
Early History
• Rome was founded in
753 B.C.
• In 509 B.C. Rome becomes a Republic
(a government with no monarch and the people vote for their representatives)
Twelve Tables
• In 451 B.C. Rome develops the Twelve
Tables
• These laws influenced future generations greatly.
Julius Caesar and the end of the
Republic
In 60 B.C., three men named Pompey, Crassus and Julius Caesar formed an alliance known as the
First Triumvirate.
• In 49 B.C., Caesar became
Rome’s first dictator.
• Caesar was assassinated in 44 B.C.
Terrible Rulers
• Caligula (37-41 A.D.) ,
Nero (54-68 A.D.), and other terrible rulers weakened the power of the Roman Empire.
The Rise of Christianity
• Around 30 A.D. Jesus Christ is crucified.
• When Rome burns in 64 A.D., Nero blames Christians and they are persecuted for the next 200 years.
• Constantine becomes the first
Christian Emperor of Rome.
• In 313 A.D., The Edict of Milan proclaimed official tolerance of
Christianity.
Christianity’s Core Beliefs
• One God.
• Jesus Christ is God’s son and the path to salvation.
• The Bible is the Holy book.
Fall of Rome
• In 395 A.D., Rome divides itself in half
(it got too big).
• In 476 A.D., the western half of the empire falls to the Visigoths.
The Legacy of Rome
Republic Government
Roman Law
Latin Language-Spanish,
Italian,French
Roman Catholic Church
Roman Engineering
•
•
Aqueducts
Sewage systems
•
•
•
Dams
Cement
Arch
Letter
• Christians were persecuted in Rome.
• Some Christians even died for their faith
(martyrs).
• Create a letter from the perspective of an imprisoned martyr where you explain your faith to a captor OR create a letter from the point of view of the Romans.
Fall of Rome
• Rome Video
• As you watch the video, answer the following two questions.
• 1. Why did Rome fall?
• 2. What will be the consequences of Rome’s fall?