PowerPoint - Ionic & Covalent - Valence, Formula, IUPAC Name
advertisement

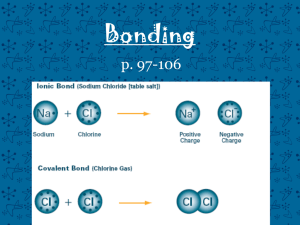
Naming Compounds What's in a name? That which we call a rose By any other name would smell as sweet." - William Shakespeare, Romeo and Juliet (II, ii) Ionic bonding Ionic bonding involves 3 steps • 1) loss of an electron(s) by one element, • 2) gain of electron(s) by a second element, • 3) attraction between positive and negative e– 1) Na 2) Cl 3) Na+ Na+ Cl– Ions Since ions are formed as a results of the movement of electrons, ionic compounds will conduct electricity when in solution Covalent bonding If two atoms have approximately the same pull on electrons, they share the electrons (forming a “covalent” bond) Rules for naming Ionic compounds MONATOMIC IONS (single atom ions) • Metal ions form positive ions : CATIONS • Metal (+ ion) comes 1st Names • Identified simply by the elements name • Negative ions : ANIONS • Drop the ending and replace with -ide. Example: sodium chloride • Do not capitalized unless starting a sentence Binary Compounds (compounds composed of two elements) • Total number of positive charges and negative charges must be equal • Use valence electrons to balance name of cation name of anion • Example: magnesium bromide Mg2+ Br1need 2 Br1- MgBr2 • Some metals form 2 or more cations with different charges • As before, positive metal comes first • The charge (valence) of the metal is indicated in brackets using roman numerals • the anion ends in –ide • e.g. Fe2+ is iron(II) Fe3+ is iron(III) Element (charge) Name Cu (1,2) copper (I) , copper(II) Fe (2,3) iron(II), iron (III) Pb (2,4) lead(II), lead(IV) Sn (2,4) tin (II), tin (IV) Co (2,3) cobalt (II), cobalt (III) Cr (2,3) chromium(II) chromium(III) Mn (2,3) manganese(II), manganese(III) Hg (1,2) mercury (I), mercury (II) Polyatomic Ions • Groups of atoms can also have valences • “Polyatomic ions” are groups of atoms that interact as a single unit • e.g. OH1-, (SO4)2-, Ba3(PO4)2 = barium phosphate • Naming compounds with polyatomic ions is similar to naming other ionic compounds • You should note that compounds with polyatomic ions have names ending in -ate or -ite not -ide • Note that most are negative, except ammonium • Name: Ca(OH)2, CuSO4, NH4NO3, Co2(CO3)3 Compounds containing polyatomic ions Ca(OH)2 CuSO4 NH4NO3 Co2(CO3)3 - calcium hydroxide - copper(II) sulfate - ammonium nitrate - cobalt(III) carbonate Practice naming Ionic compounds Give formulae & name: Ca + I, O + Mg, Na + S = Ca2I1 = CaI2 = calcium iodide = Mg2O2 = MgO = magnesium oxide = Na1S2 = Na2S = sodium sulfide Naming covalent compounds 1 mono 2 di 3 tri 4 tetra 5 penta 6 hexa 7 hepta 8 octa 9 nona 10 deca • -ide ending, each element has “prefix” • prefix refers to # of atoms - not valence N2O4 = dinitrogen tetroxide • Exception: drop mono for first element CO2 = carbon dioxide • The first vowel is often dropped to avoid the combination of “ao” or “oo”. CO = carbon monoxide (monooxide) P4O10= tetraphosphorus decoxide SO2= sulfur dioxide (doxide) • Name: CCl4, P2O3, IF7 Write and name the following covalent compounds CCl4 carbon tetrachloride P2O3 diphosporus trioxide IF7 iodine heptafluoride