Early Civilizations: Mesopotamia & Egypt Unit 1, SSWH 1 a and b
advertisement

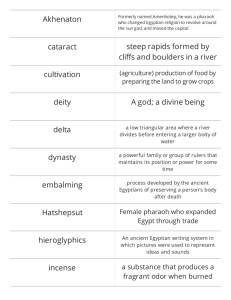
Early Civilizations: Mesopotamia & Egypt Unit 1, SSWH 1 a and b SSWH 1 a & b Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies; include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attention to Hammurabi’s law code. Describe the relationship of religion and political authority in Ancient Egypt. What were the origins and structures of Mediterranean societies? Civilization’s 5 Characteristics 1.Advanced Cities 2.Specialized Workers 3.Complex Institutions 4.Record Keeping (scribe & Cuneiform) 5.Improved Technology p.19-20 Mesopotamia • Location: Modern day Iraq & Iran Means: Land between 2 rivers (Tigris & Euphrates)…is located in the Fertile Crescent • Ziggurat—tiered, pyramid like structure that served as the center of community (more than a temple) p. 30 -32 • Culture: Cuneiform—Wedge Shapes…this was the writing system Epic of Gilgamesh—recorded stories of history • Economy: Bartering system Cultural Diffusion—Spreading culture through trade (Obsidian Jewelry & Tools) • Politics: Priests 1st leaders Dynasties—Lengthy ruling families City States—City which dominates region Law: Hammurabi’s Code – 282 written laws, created to unify the community (govt responsible for society) p.36- 37 • Religion: Foundation of Society The people worship many gods (Polytheism) Each City had its primary God of worship but all were given respect A dark bleak outlook on the afterlife…they did not make elaborate preparations Egypt: Religion • Polytheistic: believed in 2,000 + gods • Ra (sun god) & Osiris (god of the dead): IMPORTANT • Afterlife: prepared for it (saved money, food, clothes, etc. • Pyramids: Tombs built for Pharaoh • Pharaoh believed they were a god Egypt: Politics • Pharaoh: ruler of Egypt, a king • Theocracy: govt based on religious belief (Pharaoh is a god & ran the country p.44 -56 Shapely Review Draw a large triangle on your paper. On the triangle, write 3 important points you wish to remember. Be prepared to share in one minute.