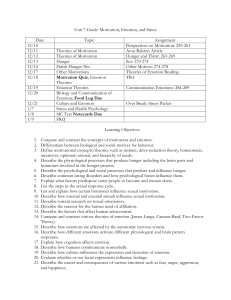
Unit 7 Guide: Motivation, Emotion, and Stress Date Topic
advertisement

Date 12/10 12/11 12/12 12/13 12/16 12/17 12/18 12/19 12/20 1/6 1/7 1/8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Unit 7 Guide: Motivation, Emotion, and Stress Topic Assignment What motivates us? Worksheet + Rock and a Hard Place article Review theories of emotion Psych Sim: Hunger and the Fat Rat + Hunger and Thirst: 263-269 Biology of Hunger Online Lecture: Psychology of Hunger Practice/Social Motives Sex: pg. 270-274 + Other Motives: pg. 274-278 Quiz; Introduction to Emotions Online Lecture: Theories of Emotion Theories of Emotion Practice; Biology Emotions: pg. 279-284 of Emotion Expressing Emotion Communicating Emotions: pg. 284-289 Specific Emotions Love Article Stress Psychology Over break: Stress Packet Stress and Health Psychology Notecards MC Test Cumulative FRQ Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the concepts of motivation and emotion. Differentiate between biological and social motives for behavior. Define motivational concepts/theories such as instinct, drive-reduction theory, homeostasis, incentives, optimum arousal, and hierarchy of needs. Describe the physiological processes that produce hunger including the brain parts and hormones involved in the hunger process. Describe the psychological and social processes that produce and influence hunger. Describe common eating disorders and how psychological forces influence them. Explain what factors predispose some people to become and remain obese. List the steps in the sexual response cycle. List and explain how certain hormones influence sexual motivation. Describe how internal and external stimuli influence sexual motivation. Describe current research on sexual orientation. Describe the reasons for the human need of affiliation. Describe the factors that affect achievement motivation. Compare and contrast various theories of emotion (James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, Two-Factor Theory). Describe how emotions are affected by the autonomic nervous system. Describe how different emotions activate different physiological and brain pattern responses. Explain how cognition affects emotion. Describe how humans communicate nonverbally. Describe how culture influences the expression and detection of emotion. Evaluate whether or not facial expressions influence feelings. Describe the causes and consequences of various emotions such as fear, anger, aggression, and happiness. Describe the biology behind emotion. Describe the three types of conflict. Describe Han’s Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS). 25. Describe the type of events that provoke stress. 26. Compare and contrast the ways in which Type A and Type B handle stress (and the consequences of this). 27. Describe how stress makes people more vulnerable to disease and what can be done to reduce stress. 28. Describe the three types of coping. Vocabulary Words 1. Motivation v. Emotion 2. Instinct 3. Drive-Reduction Theory 4. Homeostasis 5. Incentives 6. Arousal Theory 7. Yerkes-Dodson Law 8. Hierarchy of Needs 9. Hunger Hormones: Glucose, Insulin, Leptin, Orexin, Ghrelin* 10. Set Point 11. Sexual Orientation 12. Affiliation motivation 13. Achievement motivation 14. James-Lange Theory 15. Cannon-Bard Theory 16. Two-Factor Theory 17. Facial Feedback 18. Display Rules 19. Catharsis 20. Stress v. Stressor 21. General Adaptation Syndrome 22. Type A v Type B 23. Lymphocytes 24. Psychoneuroimmunology 25. Biopsychosocial Model (of stress, sex, etc.) *Connection not needed Names 1. Charles Darwin 2. Abraham Maslow 3. Virginia Johnson and William Masters 4. Paul Ekman 5. Ed Diener 6. William James and Carl Lange 7. Walter Cannon and Philip Bard 8. Meyer Friedman and Ray Rosenman 9. Richard Lazarus 10. Stanley Schachter and Jerome Singer 11. Joseph LeDoux 12. Hans Selye