Document
advertisement

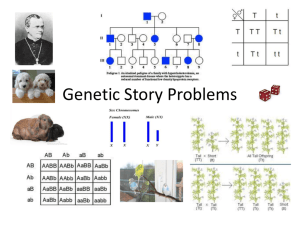
Genetics Punnett Square Practice Genetics Practice Problems • 1. For each genotype below, indicate whether it is heterozygous (Ht) or homozygous (Ho) AA Bb Cc DD Ee ff Gg HH Ii JJ kk LL Mm nn oo PP • 2. For each of the genotypes below determine what phenotypes would be possible. Consider: Purple flowers are dominant to white flowers (P) & Brown eyes are dominant to blue eyes (B) PP __________ BB __________ Pp __________ Bb __________ PP __________ bb __________ #2 Continued • Round seeds are dominant to wrinkled seeds (R). Bobtails in cats are recessive (T). RR __________ TT__________ Rr ___________ Tt __________ rr ___________ tt ___________ • 3. For each phenotype below, list the genotypes (remember to use the letter of the dominant trait) Straight hair is dominant to curly hair (S). ________ straight ________ straight ________ curly Pointed heads are dominant to round heads (H). ________ pointed ________ pointed ________ round PUNNETT SQUARES Crosses Involving One Trait • In a certain species of animal, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Using a Punnett square, predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring whose parents are both Bb, having heterozygous black fur. Genotypes: ___% homozygous black fur (BB) __ % heterozygous black fur (Bb) ___% homozygous brown fur (bb) Phenotypes: ___% black fur ___ % brown fur Now do the same when: • One parent is homozygous black and the other is homozygous brown. Genotypes: ___% homozygous black fur (BB) ___ heterozygous black fur (Bb) ___% homozygous brown fur (bb) Phenotypes ___% black fur ___% brown fur Repeat this process again when One parent is heterozygous black and the other is homozygous brown. Genotypes: ___% homozygous black fur (BB) ___ heterozygous black fur (Bb) ___% homozygous brown fur (bb) Phenotypes ___% black fur ___% brown fur Set up a Punnet square for each of the following crosses. Round seeds are dominant to wrinkled seeds 1. (Rf x rr). What percent of these offspring will be round? 2. RR x rr What percent of these offspring will be round? 3. RR x Rr What percent of these offspring will be round? 4. Rr x Rr What percent of these offspring will be round? 5. A (tall) TT plant is crossed with a (short plant) tt. What percent of the offspring will be tall? 6. A Tt plant is crossed with a Tt plant. What percent of the offspring will be short? 7. A heterozygous round seeded plant (Rr) is crossed with a homozygous round seeded plant (RR). What percent of the offspring will be homozygous (RR)? 8. A homozygous round seeded plant is crossed with a homozygous wrinkled seeded plant. What are the genotypes of the parents? _____________ x ______________ What percent of the offspring will also be homozygous? 9. In pea plants purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. If two white flowered plants are cross, What percentage of their offspring will be white flowered? 10. A white flowered plant is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for the trait. What percentage of the offspring will have purple flowers? 11. Two plants, both heterozygous for the gene that controls flower color are crossed. What percentage of their offspring will have purple flowers? What percentage will have white flowers? 12. In guinea pigs, the alleles for short hair are dominant. What genotype would a heterozygous short haired guinea pig have? What genotype would a purebred, short haired guinea pig have? What genotype would a long haired guinea pig have? 13. Show the cross for a pure breed, short haired guinea pig and a long haired guinea pig. What percentage of the offspring will have short hair? 14. Show, the cross for two heterozygous guinea pigs. What percentage of the offspring will have short hair? What percentage of the offspring will have long hair? 15. Two short haired guinea pigs are mated several times. Out of 100 offspring, 25 of them have long hair. What are the probable genotypes of the parents? _________ x Show the cross to prove it! Dragon Genetics • Remember: – UPPER CASE LETTERS REPRESENT DOMINANT ALLELES – AND – Lower case letters represent recessive alleles Dragon Genetics, cont. N = LONG NECK N = short neck E = RED EYES e = white eyes H = HORN PRESENT h = horn absent F = FIRE BREATHING f = not fire breathing G = GREEN BODY G = grey body L = LONG TAIL l = short tail S = SPIKES ON TAIL S = no spikes on tail R = RED WINGS r = yellow wings T = THREE TOES t = four toes W = YELLLOW BELLY w = white belly B = BLACK TAIL SPIKES b= red tail spikes K = FRECKLES k = no freckles X = X = NO EAR FRILLS XX = FEMALE Y = EAR FRILLS YY = MALE Dragon Genetics Questions Using the Dragon Code, answer the following questions. 1. What letters are used to represent wing color? 2. What letters are used to represent neck length? 3. The letter “Y” is used as a symbol to represent _____________________. 4. The letter “e” is used to represent ________. REMEMBER: – An upper case, or lower case letter, is used to represent a dominant trait. – A lower case, or small letter, is used to represent a recessive trait. – Dominant traits completely mask recessive traits – Refer to the Dragon key to answer the following questions. 5. List 6 dominant traits shown in the key. 6. List 6 recessive traits shown in the key. 7. Fill in the blanks Traits Genotype Neck Size NN or Nn Phenotype Neck Size Short neck Spikes on Tail No spikes Eye Color EE Horn (present or absent) Hh Fire Breathing ______ or ______ Belly Color WW or Ww Color of Spikes Tail Length Breaths fire Red ______ or ______ Long 10. Cross a male dragon with a short neck with a female dragon that is purebred for a long neck. Show percentages of offspring. 11. Cross a hybrid fire breathing dragon with a homozygous recessive non-fire breathing dragon. Show percentages of offspring. Dihybrid Cross • Example: cross between hair and eye color heterozygous pea seeds. B b E e = Black = blonde = Brown = blue BbEe x BbEe BE Be bE be x BE Be bE be possible gametes produced Punnett Squares - Dihybrid Crosses Involve the Cross of Two Traits In a dihybrid cross, when two traits are considered, the number of possible combination of the offspring increases. Suppose that Black hair (B) is dominant over blonde hair (b) and Brown eyes (E) are dominant over blue eyes (e). Whqt percent of offspring could be expected to have blonde hair and blue eyes if; 1. The father has black- hair (heterozygous) and brown eyes (heterozygous) and the mother has blonde hair and blue eyes. • Genotype of father— BbEe • Genotype of mother— bbee • Copy the following Punhett square, then, fill in the boxes. Dihybrid Cross Dihybrid Cross _______/______: __ _______/______: __ _______/______: __ _______/_______: __ _________ phenotypic ratio