SBI3U Problem Solving Questions
advertisement
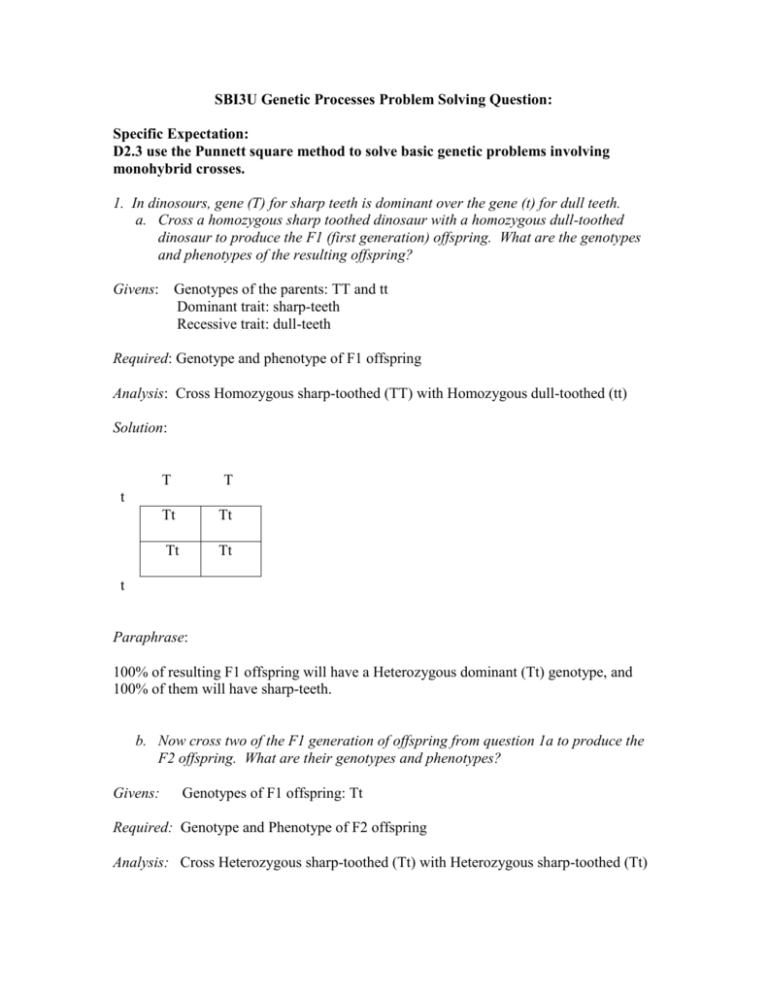
SBI3U Genetic Processes Problem Solving Question: Specific Expectation: D2.3 use the Punnett square method to solve basic genetic problems involving monohybrid crosses. 1. In dinosours, gene (T) for sharp teeth is dominant over the gene (t) for dull teeth. a. Cross a homozygous sharp toothed dinosaur with a homozygous dull-toothed dinosaur to produce the F1 (first generation) offspring. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the resulting offspring? Givens: Genotypes of the parents: TT and tt Dominant trait: sharp-teeth Recessive trait: dull-teeth Required: Genotype and phenotype of F1 offspring Analysis: Cross Homozygous sharp-toothed (TT) with Homozygous dull-toothed (tt) Solution: T T Tt Tt Tt Tt t t Paraphrase: 100% of resulting F1 offspring will have a Heterozygous dominant (Tt) genotype, and 100% of them will have sharp-teeth. b. Now cross two of the F1 generation of offspring from question 1a to produce the F2 offspring. What are their genotypes and phenotypes? Givens: Genotypes of F1 offspring: Tt Required: Genotype and Phenotype of F2 offspring Analysis: Cross Heterozygous sharp-toothed (Tt) with Heterozygous sharp-toothed (Tt) Solution: T t T TT Tt Tt tt t Paraphrase: 25% of the F2 offspring will have Homozygous dominant (TT) genotypes, 50% will have Heterozygous dominant (Tt) genotype and 25% will have Homozygous recessive (tt). 75% of the F2 offspring will have sharp-teeth and 25% will have dull-teeth. SBI3U Cellular Biology Problem Solving Question: Specific Expectations: B2.2 Investigate the effect of various qualitative factors on the rate of diffusion of molecules across a plasma membrane B3.4 Explain the importance of various cellular processes in human systems B2.1 Use appropriate terminology related to cellular biology, including but not limited to: macromolecules, passive transport, active transport, catalyst, and fluid mosaic model 1. A marathon runner collapses after running on a hot day. Although the runner consumed adequate water along the route, blood testing showed that many of his red blood cells had burst. Why was this the case? Provide a diagram to illustrate what happened. Analysis: Review and understand key concepts: 1. The law of diffusion (the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration) 2. Two types of solutions: Hypotonic (A solution which is more dilute ie. less solutes than the cytosol. The cell gains water and swells.) Hypertonic (A solution which is more concentrated ie. more solutes than the cytosol. The cell loses water and shrinks.) Solution: The marathon runner is a case of a hypotonic solution. The solute concentration is higher inside of his red blood cells than the outside. This causes water to move inside of the cells, causing them to swell and burst.