reproduction homozygous
advertisement

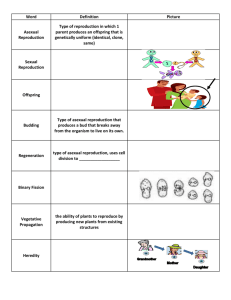
Student Name _________________________________ Our Genes Our Selves Unit Review 1. Offspring that are the result of sexual reproduction are _______________ to their parents. 2. How are traits determined? 3. What occurs during sexual reproduction? 4. Are humans the only organisms that reproduce sexually? 5. What part of the cell contains the genetic information? 6. Why did Mendel study pea plants? 7. What kind of plants (homozygous or heterozygous) did Mendel use? Why? 8. What causes inherited diseases? 9. What is an example of asexual reproduction? 10. What is the only reason an offspring of asexual reproduction is not identical to the parent? 11. Define Homozygous and Heterozygous. 12. Define Genotype and Phenotype. Student Name _________________________________ Our Genes Our Selves Unit Review 13. Create a Punnett Square that shows the results of a homozygous dominant plant crossed with a heterozygous parent. What is the ratio of dominant to recessive offspring? 14. To determine a trait, what percentage of genes come from each parent? 15. When you look at a pedigree, how can you tell if a genetic condition is dominant or recessive? 16. Who is known as the father of modern genetics? 17. What is a carrier? 18. If two parents are both carriers for a genetic trait, what are the chances that they will pass on this trait to their offspring? Use a Punnett Square to show your answer. 19. What is a dominant trait? Student Name _________________________________ Our Genes Our Selves Unit Review 20. What is a genetic mutation? 21. Breeding of humans cannot be done in laboratories. What methods are used to help understand human genetics? 22. What kind of plants did Gregor Mendel use? 23. What is an allele?