Lecture 18 Basics: Genes and Alleles 18.1 Basic vocabulary Gene
advertisement
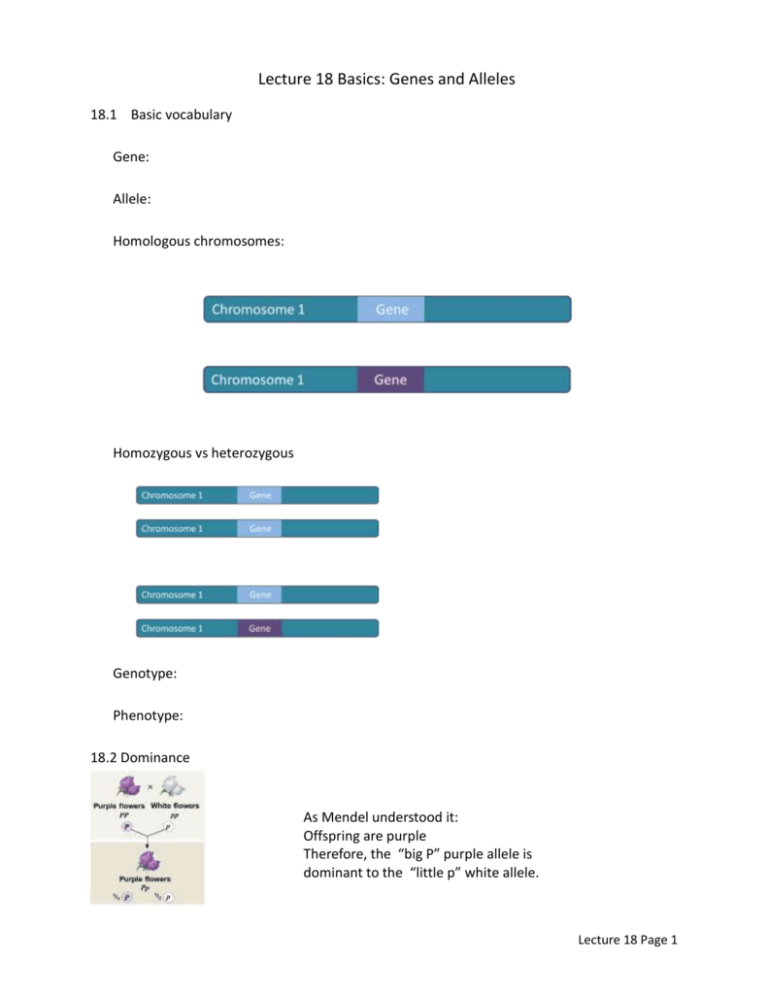
Lecture 18 Basics: Genes and Alleles 18.1 Basic vocabulary Gene: Allele: Homologous chromosomes: Homozygous vs heterozygous Genotype: Phenotype: 18.2 Dominance As Mendel understood it: Offspring are purple Therefore, the “big P” purple allele is dominant to the “little p” white allele. Lecture 18 Page 1 Dominance Explained: Pigment that causes purple color: anthocyanin 2 Genes: transcription factor on one chromosome, enzyme gene on another chromosome The “Big P” allele The “Little p” allele Lecture 18 Page 2 18.3 Homozygotes and heterozygotes Homozygous PP Homozygous pp Heterozygous Pp Dominant allele: Recessive allele: 18.4 Punnett Squares Lecture 18 Page 3 Punnet Square Practice: Book question 14-6 A pea plant heterozygous for inflated pods (Ii) is crossed with a plant homozygous for constricted pods. Draw a Punnett square for this cross. What percentage of the offspring will have constricted pods? Genotype is different from phenotype Lecture 18 Page 4 18.5 The Test cross: determines genotype in an organism showing the dominant trait Given an unknown: Solution: cross unknown against __________________________________________ Offspring if PP: Offspring if Pp: Lecture 18 Page 5 Practice problems: 1. In pea plants, spherical seeds (S) are dominant to dented seeds (s). In a genetic cross of two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? ________________ 2. In guinea pigs, short hair is dominant to long hair (S,s). Use a Punnett square to determine the following. a. One guinea pig has long hair, the other is a heterozygote. What proportion of the offspring will have short hair? ________________ b. A litter of guinea pigs all have short hair. One parent has short hair, the other long hair. What is the genotype of the short haired guinea pig? ________________ 3. In humans, being a tongue-roller is dominant over non-roller (R, r). A man who is a non-roller marries a woman who is a heterozygous for tongue-rolling. a. What is the father’s phenotype? ________________ b. What is the father’s genotype? ________________ c. What are the possible gametes the father can give his offspring? ________________ d. What are the possible gametes the mother can give her offspring? ________________ e. What is the probability their child will be a tongue-roller? ________________ f. They have a child who is a tongue-roller. If she marries a man who is a non-roller, what is the probability their child will be a tongue-roller? ______________ Lecture 18 Page 6