Ch 3 Study Guide
advertisement

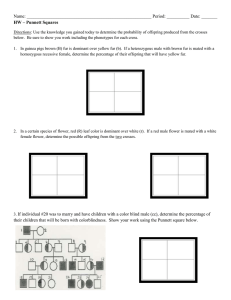
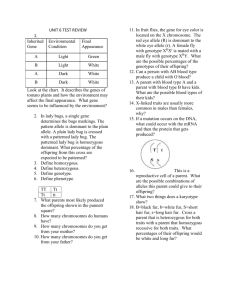
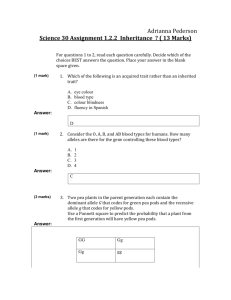
The Science of Heredity Study Guide Name__________________________________________________Class__________________ 1. What are genes? 2. What is phenotype? 3. What does the notation TT mean to geneticists? 4. What is a hybrid? 5. What does a Punnett square show? 6. What does the notation Tt mean to geneticists? 7. What is the probability of producing a tall pea plant from a genetic cross between two hybrid tall pea plants? 8. If a homozygous black guinea pig (BB) is crossed with a homozygous white guinea pig (bb), what is the probability that an offspring will have black fur? 9. Where does protein synthesis take place? 10. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 11. The different forms of an allele are called____________________________. 12. Walter Sutton discovered that the sex cells of grasshoppers have__________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 13. When sex cells combine to produce offspring, each sex cell contributes____________________________________________________________________. 14. What do transfer RNA molecules do during protein synthesis? 15. What is a trait? 16. What happens during meiosis? 17. What do messenger RNA molecules do during protein synthesis? 18. What is genotype? 19. Chromosomes are made up of_____________________________________. 20. Which nitrogen base in RNA is not part of DNA? 21. What is a heterozygous organism? 22. What is a homozygous organism? 23. Know what lower case and capital letter represent? 24. What does incomplete dominance or codominance mean? 25. Explain the function of meiosis. 26. Explain why Mendel’s cross of purebred tall and short pea plants resulted in only tall plants. 27. Be able to read, understand and predict the probability of offspring outcomes on a Punnett square. B= black fur b= white fur B b Which trait is controlled by a dominant allele? Which is controlled by a recessive allele? b What is the genotype of the offspring? Phenotype? b What percent will have black fur? White fur?