TISSUES
advertisement
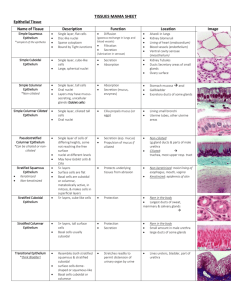
TISSUES HONORS ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Tissues & Homeostasis • 4 basic types of tissues in human body contribute to homeostasis by providing diverse functions including • protection • support • communication among cells • resistance to disease • & many more Definition • a tissue is a group of similar cells that usually have a common embryonic origin & function together to carry out specialized activities Tissues • their structure & properties are influenced by factors such as: – nature of the extracellular material surrounding tissue cells – type of connections between cells Classification of Tissues 1. Epithelial – – covers body surfaces & lines hollow organs, cavities, & ducts forms glands 2. Connective – protects & supports 3. Muscular – movement 4. Nervous – detects changes in/out body & responds by generating action potentials Embryology of Tissues 1. Epithelial – from all 3 layers 2. Connective – mesoderm 3. Muscular – mesoderm 4. Nervous – ectoderm Cell Junctions • are contact pts between plasma membranes of adjacent cells • found between most epithelial cells & some muscle & nerve cells Surfaces of Cells Basement Membrane (bm) • thin, extracellular layer • commonly has 2 parts: 1. basal lamina 2. reticular lamina Covering & Lining Epithelium • classified according to 2 characteristics: 1. # of layers • single layer = simple • multiple layers = stratified • single layer that looks like multiple = psuedostratified 2. cell shape • squamous • cuboidal • columnar Simple Epithelium 1 layer of cells, often in sheets functions: diffusion/osmosis filtration secretion: production & release of substances (sweat, mucus) • absorption: intake of fluids or other substances • • • • • Pseudostratified Epithelium • appears to have multiple layers because: 1. nuclei @ different layers 2. not all cells reach apical surface Stratified Epithelium • 2 or more layers of cells – named by shape of top layer • function: protection where there is considerable wear & tear Squamous Cells • arranged like floor tiles • very thin: allows for rapid passage of substance thru cell Cuboidal Cell • shaped like cubes or hexagons • +/- microvilli on apical surface – finger-like cytoplasmic projections – function increase surface area • function: secretion or absorption Columnar Cells • taller than they are wide • +/- microvilli or cilia on apical surface – cilia: tiny hair-like projections that beat in unison: moves substances across surface of cell • • • • function: protection absorption secretion Simple Squamous Epithelium • single layer flat cells • viewed from – apical surface looks like tiled flooring – cross-section: fried eggs cross section Simple Squamous Epithelium • found: • @ sites where filtration (kidneys) or diffusion (lungs, capillaries) occur • lines blood vessels & chambers in heart (endothelium), forms lining for serous membranes (mesothelium) Simple Cuboidal Epithelium • nuclei round & centrally located • functions: – secretion – absorption • found in: – thyroid gland – kidneys Simple Columnar Epithelium • 2 forms: nonciliated/ciliated • nonciliated simple Columnar Epithelium – 2 types: 1. Columnar epith. w/microvilli on apical surfaces 2. Goblet cells • produce & secrete mucus Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium • cilia on apical surface • +/- Goblet cells • functions: – move mucus or any foreign objects away from lower respiratory tract or ova towards uterus • found in: – airways of upper respiratory system – fallopian (uterine) tubes Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium • all cells attached to bm but not all reach apical surface • Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epith.: • cells that do reach apical surface either are goblet cells or are ciliated • Nonciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epith: • no cilia or goblet cells Stratifed Squamous Epithelium • basal layer continually undergoing cell division – as new cells grow, cells near base pushed upward – as near apical border moving farther away from their blood supply (in underlying connective tissue) dehydrate, shrink, harden, die cell jcts break down cells sloughed off Stratified Squamous Epithelium • upper layers contain keratin: tough, fibrous protein that protects underlying tissues from heat, microbes, chemicals • found: skin • found: lining mouth (buccal mucosa) & esophagus • protect underlying tissues from wear & tear and from invasion by microbes • Keratinized • Nonkeratinized Glandular Epithelium • gland: single cell or group of cells that secrete substances into: – ducts – onto a surface – into blood • classified: 1. endocrine – secretions intercellular fluid capillary 2. exocrine – secretions ducts surface of skin or lining of hollow organ Classification of Glands Connective Tissue (CT) • most abundant & widely distributed tissue in body • 2 basic elements: 1. extracellular matrix 2. cells Extracellular Matrix • greater % in CT than other tissues • it’s the material located between cells (secreted by those cells) • determines qualities of the CT • not usually found on surfaces, usually rich blood supply (x cartilage & tendons) • consists of: – protein fibers – ground substance CT Cells • immature form suffix “blast” – large capacity to divide – secrete matrix • mature form suffix “cyte” – less likely to divide – maintain matrix Fibroblasts • large flat cells w/ branching processes • found in most CT • migrate thru CT secreting fibers & ground substance Macrophages • develop from monocytes • phagocytes • irregular shape • 2 types: 1. wandering – move to sites of infection or inflammation 2. fixed – – reside in a particular tissue ex: alveolar macrophages Plasma Cells • small cells that develop from B lymphocytes • Important in immune response • most reside in CT – GI & respiratory tracts – lymph nodes, spleen, red bone marrow Mast Cells • found along side blood vessels that supply CT • produce & secrete histamine: dilates small blood vessels as part of inflammatory response (reaction to injury or infection) • can also bind, ingest, & kill bacteria Adipocytes • aka adipose cells or fat cells • store triglycerides • functions: – store fats for nrg – insulate – cushion organs Ground Substances • acellular component of CT that supports cells, binds them together, stores water, provides medium thru which substances are exchanged between blood & cells • may be: • fluid • semifluid • gelatinous • calcified CT Fibers: 3 Types 1. Collagen – – “colla” = glue a protein (25% of all protein in body!) very strong fibers that resist pulling 2. Elastic – – – smaller strong but stretchy fibers made of protein called elastin plentiful in skin, blood vessel walls, lung tissue 3. Reticular – – made of collagen in fine tubes coated with glycoproteins forming branching networks & found in BM skin, adipose, reticular CT (spleen, lymph nodes) Mature CT: Loose CT 1. Areolar CT • 1 of most abundant types • includes all types of CT cells & fibers • found in: subcutaneous tissue Mature CT: Loose CT 2. Adipose Tissue • cells: adipocytes • found ass’c with areolar CT • 2 types: 1. white – most of the adipose in adults 2. brown – – darker due to rich blood supply widespread in newborns: helps maintain body temperature Mature CT: Dense CT • contains more numerous fibers but fewer cells than in loose CT • 3 types: 1. Dense Regular CT 2. Dense Irregular CT 3. Elastic CT Dense Regular CT • collagen fibers lined up in parallel pattern allowing it to withstand pulling aling axxis of fibers: very strong tissue • silvery white, tough • ex: tendons & most ligaments Dense Irregular CT • collagen fibers irregularly arranged • found where pulling forces exerted in various directions • found: dermis, pericardium, periosteum Elastic CT • predominate fiber: elastic fibers • quite strong & able to return to original shape after being stretched • found: elastic arteries, lungs Membranes • are flat sheets of pliable tissue that cover or line a part of the body • 2 types: 1. epithelial membrane: – – epithelial layer + underlying CT types: mucous membrane, serous membrane, cutaneous membrane (skin) 2. synovial membrane: – – + CT but - epithelium line joints Mucous Membranes (Mucosa) • line body cavities that open directly to exterior • line: entire digestive, upper respiratory, & reproductive tracts • cells connected by tight jcts • Goblet cells secrete 1. mucus slippery so prevents cavities from drying out 2. enzymes from some 3. site of nutrient absorption Serous Membranes (Serosa) • line cavities that do not open directly to exterior & covers organs w/in those cavities • made of: areolar CT covered by mesothelium (simple sq. epith.) which secretes serous fluid • 2 layers: 1. parietal peritoneum – covers cavity wall 2. visceral peritoneum – – – covers organs in pericardial cavity = pericardium in abd. Cavity = peritoneum CARTILAGE • consists of a dense network of collagen (strength) & elastic (flexibility) fibers, no blood vessels or nerves (x perichondrium) so heals very slowly • chondrocytes: mature cartilage cells – occur singly or in small groups w/in space called lacunae • perichondrium: membrane of dense CT – covers surface of most cartilage Cartilage • 3 types: 1. Hyaline cartilage – – most abundant cartilage in body, also the weakest provides flexibility & support 2. Fibrocartilage – – no perichondrium provides strength & rigidity (strongest of the 3) 3. Elastic cartilage – – + elastic fibers provides strength & elasticity Bone Tissue • aka osseous tissue • 2 types: 1. Compact bone 2. Spongy bone Compact Bone • basic unit of compact bone is the osteon (haversian system) • has 4 parts: 1. Lamellae – – concentric rings of extracellular material & collagen make bone hard & strong 2. Lacunae 3. Canaliculi 4. Central (haversian) canal) Spongy Bone • lacks osteons • found only inside compact bone • consists of columns of bone called trabeculae – spaces between trabeculae filled with red bone marrow Blood • liquid CT made up of: • Plasma – liquid portion of blood (yellow) – water, dissolved nutrients, wastes, plasma proteins, hormones, gases, ions • RBCs: transport O2 • WBCs: phagocytes, immune response, allergic reactions • Platelets: cell particles involved in blood clotting Muscular Tissue • consists of elongated cells called muscle fibers that can use ATP to generate force movement, maintain posture, generate heat • 3 types: 1. Skeletal 2. Smooth 3. Cardiac Skeletal Muscle Tissue • most attached to a bone • muscle fibers up to 12-16 in in longest muscles: – multinucleated (on edges) – striated – voluntary Smooth Muscle Tissue • in walls of hollow internal structures – blood vessels – urinary bladder – intestines • muscle fibers small, 1 centrally located nuclei, +/- gap jcts – nonstriated – involuntary Cardiac Muscle Tissue • forms wall of heart • muscle fibers are branched with 1 centrally located nuclei – striated – involuntary – *intercalated discs: attach individual fibers end-to-end (desmosome + gap jct) allows for quicker conduction of action potentials coordinated contractions of heart chambers Nervous Tissue • 2 cell types: 1. neurons – nerve cells that can generate action potentials which are conducted to other neurons, muscles, or glands 2. neuroglia (glia) – supportive cells to neurons – cannot generate action potentials Neurons Action Potentials • electrical excitability: ability to respond to certain stimuli by producing electrical signals (action potentials) • in neurons: travel (propagate) along plasma membrane release of neurotransmitter • in muscle fibers: action potentials cause the fiber to contract (shorten) Medical Terminology • atrophy: decrease in size of cells decrease in size of organ • hypertrophy: increase in size of a tissue because its cells enlarge w/out undergoing cell division