Chapter 5
advertisement

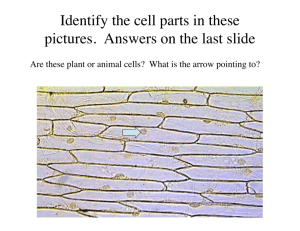
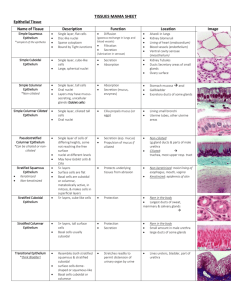
Anatomy and Physiology 101: Chapter 5, Tissues I. Introduction A. Define “Tissue” B. The Science of tissues is called: C. Cellular Junctions 1.Define “Tight junctions” and provide an example: 2. Define “Desmosomes” and provide an example: 3. Define “Gap Junctions” and provide an example: II. Epithelial Tissues A. Provide 3 characteristics of epithelial tissues 1. 2. 3. B. Draw a typical epithelium with one layer of cells. Label the basement membrane, the apical surface, and the basal surface. C. Classifications of Epithelium 1.List the two terms used to classify epithelium based on the number of cell layers. a. b. 2.List the three terms used to classify epithelium based on their shapes. a. b. c. D. Types of Epithelium: For each of the following, list a function and a location 1. Simple Squamous Epithelium a. Function: b. Location: 2.Simple Cuboidal Epithelium a. Function: b. Location: 3.Simple Columnar Epithelium a. Function: b. Location: 4.Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium a. Function: b. Location: 5.Stratified Squamous Epithelium a. Function: b. Location: c. Distinguish between keratinized and unkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, and provide a location for each type: a. Keratinized: b. Unkeratinized: 6. Transitional Epithelium a. Function: b. Location: 7.Glandular Epithelium a. Define “exocrine gland, and provide 1 example of an exocrine gland. b. Define “endocrine gland” and provide 1 example of an endocrine gland. 8. Additional Structures a. Distinguish between Cilia and Microvilli: a. Cilia: b. Microvilli: b. What is the function of goblet cells? III. Connective Tissue(CT) Overview A. List 4 characteristics of connective tissue 1. 2. 3. 4. B. Fixed and Wandering cells – distinguish between the two, and give an example of each: 1. Fixed Cells: 2. Wandering Cells: C. CT Fibers: Name, characteristic, and one location for each. 1. 2. 3. D. List 3 Types of Loose CT 1. 2. 3. E. List 3 Types of Dense CT 1. 2. 3. F. List three types of specialized CT 1.– 2.– 3.IV. Types of Connective Tissues: A. Areolar 1.Cells: 2.Fibers: 3.Location: B. Adipose 1.Cells: 2.Function: 3.Locations: C. Reticular 1.Fibers: 2.Function: 3.Locations: D. Dense Regular CT 1.Cells: 2.Fibers: 3.Function: 4.Locations (Distinguish between a tendon and a ligament): 5.Blood Supply and Healing: E. Dense Irregular CT 1.Fibers: 2.Function: 3.Location: F. Elastic CT 1.Cells: 2.Fibers: 3.Locations: G. Cartilage 1.Overview a. Cells: b. Cavities: c. Matrix: 2.Types a. Hyaline Cartilage a. Fibers: b. Locations: b. Elastic Cartilage a. Fibers: b. Locations: c. Fibrocartilage a. Fibers: b. Locations: H. Bone 1.Matrix a. Salts: b. Fibers: 2.Cells a. __________________ cells form new bone b. __________________ are bone cells c. __________________ are white blood cells that break down, or resorbs bone. I. Blood 1.Matrix: 2. Cells: a. b. c. V. Muscle Tissue A. Skeletal Muscle 1.Locations: 2.List three characteristics of skeletal muscles: a. b. c. B. Smooth Muscle 1.Locations: 2.List three characteristics of smooth muscles: a. b. c. C. Cardiac Muscle 1.Location: 2.List four characteristics of cardiac muscles a. b. c. d. D. Which type of muscles is voluntary? Which are under involuntary control? VI. Nervous Tissue A. Distinguish between neurons and neuroglia: B. List three functions of nervous tissue: 1. 2. 3. C. List three locations of nervous tissue: 1. 2. 3.