Origins of the American Revolution & Constitution
advertisement

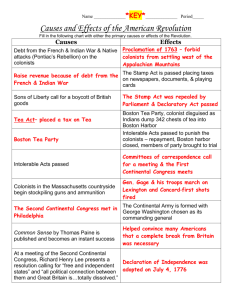
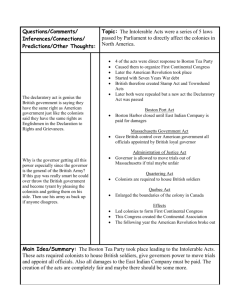
American Federalism Timeline—Government Pre-Revolutionary War 1760s—With Great Britain’s victory over France in the French and Indian War, King George III issues a series of Acts intended to tax colonists to pay off debt from the war Sugar Act Stamp Act Townshend Acts Colonists react by trying to petition Parliament to repeal the Acts Then, they begin to protest or boycott goods that are taxed such as paper goods (Stamp Act) Boston Tea Party 1770s—Parliament issues a tax on tea (The Tea Act) Colonist resistance culminates in Boston with the Sons of Liberty boarding an East India Company ship and destroying all of its shipments of tea Many colonists believed that they lacked legal representation in the British Parliament: “No taxation without representation” Intolerable Acts Named Coercive Acts issued by British Parliament to stop colonial protests and restore order after the Boston Tea Party Purpose: to punish colonists, those specifically in Mass. for destroying the tea and money wasted Colonist Reaction: violation of British Constitutional rights and natural rights Effects: Boston’s port was closed Limited governmental activities in Mass. Allowed accused royal officials to move trial locations Allowed the governor to quarter British soldiers in unoccupied buildings First Continental Congress (1774) Intolerable Acts were intended to isolate radicals like the Sons of Liberty; It backfired and created sympathies from other colonies for Mass. 12 of 13 colonies’ representatives (No Georgia) met in Philadelphia to discuss issues with British rule Results: They decided to boycott British products (Continental Association) to reverse the Intolerable Acts Also pledged support and aid for Mass. if attacked Battles at Lexington & Concord (1775) Officially recognized as the start of the American Revolutionary War All colonies (not Georgia) became involved because of the Continental Association Second Continental Congress Reconvening of the first members to take on the war effort Voted to create a Continental Army with George Washington as its commander Olive Branch Petition Delegate, Thomas Jefferson, drafted a petition to British Parliament to reconcile with King George III Re-written by delegate, John Dickinson, stating that they wanted to avoid war and create new trade and taxation terms to alleviate tension with the British….not independence A letter from John Adams, another delegate suggested discontent with the petition and stated war with Britain was inevitable Petition was rejected on grounds that it was insincere (because of Adams’ letter) Second Continental Congress No legal authority to govern as central government of the colonies Wasn’t able to move forward with independence without authorization from each colony The Road to Independence Virginia called for an official declaration of independence, formation of foreign alliances, and confederation of states International pressure to form alliances abroad meant finding a way to prove the Continental Congress credible and independent = Declaration of Independence & Articles of Confederation Declaration of Independence (1776) A statement issued by Continental Congress to the world stating and explaining that the United States of America is independence Drafted by Thomas Jefferson and company Included the colonial grievances of King George to justify independence and the right to revolution The Revolutionary War (17751783) War began between the 13 Colonies & Great Britain After persuading France to intervene on the side of the colonies, the sides were then evenly matched SPOILER: The Americans win! Results in recognition of American Independence by European powers (Old World) Articles of Confederation An agreement made between the 13 colonies that created a system of government, a confederation, and acted as the country’s first constitution Drafted by Continental Congress around 1776-1777 Ratified by all states in 1781