Unit 6 Imperialism Vocab
advertisement

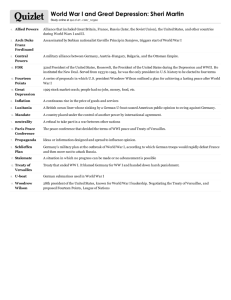
Unit 6 Imperialism Vocab Industrial Revolution O The period that saw the transition to new manufacturing processes and new forms of machinery. Lasted from 1760 to sometime between 1820 and 1840. Nationalism O patriotic feeling, principles, or efforts. Imperialism O a policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force. Woodrow Wilson O 28th President of the United States; led the United States in World War I and secured the formation of the League of Nations (1856-1924) Franz Ferdinand O Austrian archduke whose assassination by a Serbian nationalist sparked World War I. Wilhelm 11 O last German Emperor and King of Prussia, ruling the German Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia from 15 June 1888 to 9 November 1918. Lenin O Russian revolutionary leader: Soviet premier 1918–24. Lloyd George O British Prime Minister of the Wartime Coalition Government (1916–22), during and immediately after the First World War Clemenceau O French politician who served as prime minister (1906-1909 and 1917-1920) and played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Versailles (1919). Lusitania O a British luxury liner sunk by a German submarine in the North Atlantic on May 7, 1915: one of the events leading to U.S. entry into World War I. Unrestricted Submarine Warfare O a type of naval warfare in which submarines sink vessels such as freighters and tankers without warning Zimmermann Telegram O A secret German communication sent to Mexican officials asking Mexico to go to war with the United States Central Powers O Germany and its allies (Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire) in World War I. Triple Entente O Alliance between Russia, France, and Great Britain during the First World War. Later the United States would join this group. Trench Warfare O a type of combat in which opposing troops fight from trenches facing each other. La Revanche O a usually political policy designed to recover lost territory or status Marne O A river in France and the site of a World War I battle in northwestern France where the Allies defeated the Germans in 1918 Verdun O A city in France and site of a a battle in World War I (1916); in some of the bloodiest fighting in World War I the German offensive was stopped Armistice O an agreement made by opposing sides in a war to stop fighting for a certain time; a truce. Treaty of Versailles O one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. War Guilt Clause/ Article 231 O he opening article of the reparations section of the Treaty of Versailles, it blamed Germany for the war