Lab Density
advertisement

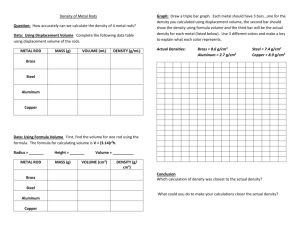
Name_________________________________________ Date__________________Period_____________ Density Lab Purpose: Using density to determine the materials of different objects (metals). Background: A block of metal is much heavier than the same size block of styrofoam. Density is a physical characteristic that describe how much mass is in a given volume of a material expressed as gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). Density is independent of size and shape and remained constant as long as you have the same material. Archimedes used this principal to determine if objects are pure gold or not. Materials: Triple-beam balance, 100ml plastic graduated cylinder, pennies, brass rod, silver rod, rulers, metal cubes Procedure: Part 1 1. Weight 3 pennies record then weight 6 pennies and record. 2. Weight the Yellow rod, record 3. Weight the Silver rod, record 4. Use the graduated cylinder & water and find a way to figure out the volume of the metallic rods and the pennies. 5. Your volume of 1ml from the graduated cylinder is equals to 1 cm3 6. Calculate the density of these objects Data: Objects 3 Pennies Weight (g) Volume (cm3) Density (D = M/V) 6 Pennies Yellow Rod Silver Rod Conclusion Questions: 1. Are the density different for 3 pennies and 6 pennies? Explain why or why not. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Which item above had the highest density?_____________________________________________________ 3. What is an alloy? (May have to search online for this answer) Is the density of alloys always the same? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Bronze is an alloy, what are some of the advantages of alloys?______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which of the items above are alloys?__________________________________________________________ 6. Which is more dense: the yellow rod or the silver rod? Explain why (*Hint: include your data in the answer) __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Draw a picture of what you think might be inside the rods that makes it dense. (*Hint: Think molecular) Yellow rod Silver rod 8. What would happen to the mass of the Yellow rod if we were to cut it in half? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What would happen to the volume of the Yellow rod if we were to cut it in half? a. Write down the new volume ____________________________ b. Use the mass you wrote down in #8 and the volume in #9a to calculate the new density of the half-rod. What do you notice? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Procedure: Part 2 1. Obtain 4 different cubes from Mr. Vu 2. Write a short description of the cubes in your data table so you know which cube it is 3. Weight each cube and record them 4. Use a ruler to measure its sides in centimeter (be as accurate as you can since wrong measurement will throw off your data and ultimately your conclusion) 5. Calculate the volume based on your measurements 6. Calculate the density of each cube 7. Use the known metal density table to figure out which material your cubes are made from Table 2: Data for Metallic Cubes Cube # Description of the Cube 1 Weight (g) Volume (cm3) Density (g/cm3) 2 3 4 Table 3: Known Density for Common Metals Metal Density (g/cm3) Metal Aluminum 2.70 Mercury Calcium 1.54 Zinc Iron 7.87 Gold Cobalt 8.89 Lead Nickel 8.91 Uranium Copper 8.96 Tin Germanium 5.32 Silver Palladium 12.0 Neodymium Platinum 20.45 Titanium Density (g/cm3) 13.53 7.14 19.32 11.34 18.97 7.31 10.49 7.01 4.51 Material