Worksheet 36 - Thermal Processes (Review
advertisement
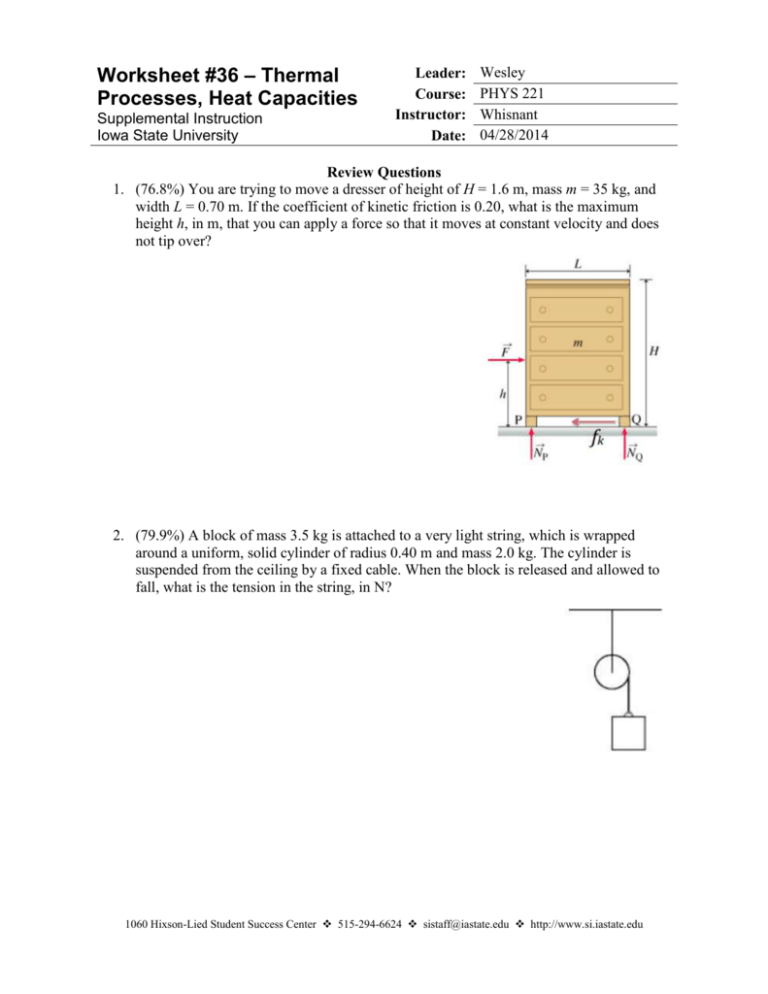
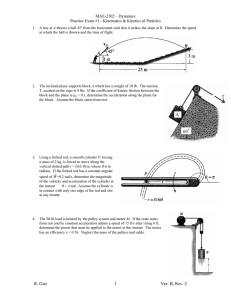
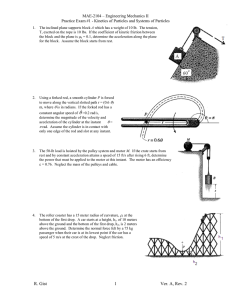
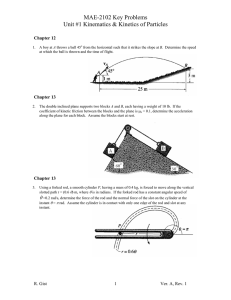
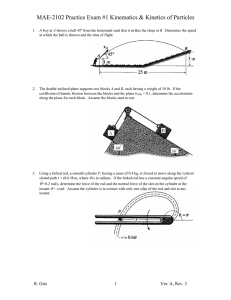
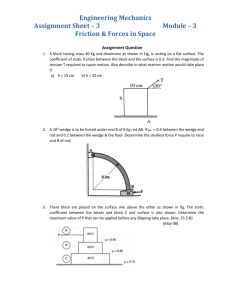
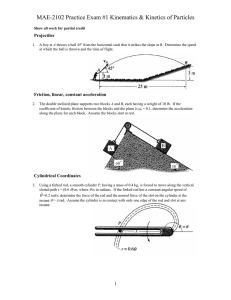
Worksheet #36 – Thermal Processes, Heat Capacities Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Wesley PHYS 221 Whisnant 04/28/2014 Review Questions 1. (76.8%) You are trying to move a dresser of height of H = 1.6 m, mass m = 35 kg, and width L = 0.70 m. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20, what is the maximum height h, in m, that you can apply a force so that it moves at constant velocity and does not tip over? 2. (79.9%) A block of mass 3.5 kg is attached to a very light string, which is wrapped around a uniform, solid cylinder of radius 0.40 m and mass 2.0 kg. The cylinder is suspended from the ceiling by a fixed cable. When the block is released and allowed to fall, what is the tension in the string, in N? 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu Do NOT plug in numbers until you have solved for the desired variable! Try to solve each problem algebraically first. 3. (62.0%) A rod of length 2.4 m and mass 7.5 kg is hinged at one end so that the rod can rotate without friction as shown. If the rod is released from rest in the horizontal position, what is its angular velocity, in rad/s, when it reaches the vertical position? Today’s Topics 1. (Thermal Processes) The temperature of of .150 moles of an ideal gas is held constant at 77.0 degrees C while its volume is reduced to 25% of its initial volume. The initial pressure of the gas is 1.25 atm. a. Determine the work done by the gas. b. What is the change in its internal energy? c. Does the gas exchange heat with its surroundings? If so, how much? Does the gas absorb or release heat? Do NOT plug in numbers until you have solved for the desired variable! Try to solve each problem algebraically first. 2. (Adiabatic Processes) Two moles of carbon monoxide (CO) start at a pressure of 1.2 atm and a volume of 30 liters. The gas is then compressed adiabatically to 1/3 of this volume. Assume that the gas may be treated as ideal. What is the change in internal energy of the gas? How does the temperature relate to this change?