Week 2 - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

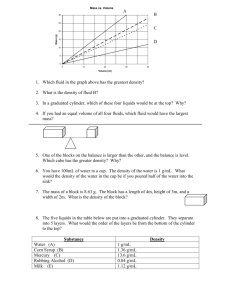
Week 2 1. Graduated cylinders are marked in units of a. b. c. d. Grams Meters Millimeters Milliliters 2. Which is the metric unit for measuring mass? a. b. c. d. foot pound kilogram ounce 3. Density is a good way to identify an object because a. Different masses of the same object will always have different densities b. Different masses of the same object will always have the same density. c. The same volume of the same object will always have different densities. d. The same masses of two different objects will have the same density 4. Joseph measures out 25 mL of distilled water for his chemistry experiment. How many liters of water is this? A. B. C. D. 0.25 L 0.025 L 2.5 L 2.5 x 10-3 L 5. Identify the correct way to write 0.00542 in scientific notation A. B. C. D. 5.42 X 10-3 5.42 X 10-4 5.42 X 102 5.42 X 104 6. A lizard has a mass of 0.98 grams. What is the mass of the lizard in milligrams? A. B. C. D. .00098 mg 9.80 mg 98 mg 980 mg 7. Which property of matter is determined by measuring the pull of gravity on a sample of matter? A. B. C. D. Weight Mass Volume acceleration 8. A teacher gives a student a metal bar. The teacher asks the student to calculate the bar’s volume using the formula V = l x w x h. The bar is 3.5 cm long, 10 mm high, and 2.0 cm wide. What is the volume of the bar in cm3? A. B. C. D. 0.7 cm3 7 cm3 70 cm3 700 cm3 9. Which of the following represents a quantitative statement about the mass of an object? A. The object is heavier than wood B. The mass of the object is 23.5 grams C. The object’s mass indicates that it has a high density D. A balance can be used to quantitatively determine the mass of an object. 10. The mass of a graduated cylinder and water is 68.0 g. After a stone was lowered into the graduated cylinder, the water level rose 30.0 mL and the mass of the cylinder, water and stone was 78.0 g. What is the density of the stone? A. 2.00 g/mL B. 10.0 g C. 0.33 g/mL D. 5.00 mL Pre-lab questions: 1. What is the equation that relates density, mass, and volume? 2. How can we use density values to determine an unknown substance? 3. Why do we need to measure irregularly shaped objects by water displacement? 4. Why is it important that a wet object be dried before finding its mass? 5. Why should you tilt a graduated cylinder when you drop in objects? 6. Do any of the metals shown in the table have a density less than water? 7. Copy down 2 data tables and label them “Table 1. Pre-1982 pennies” and “Table 2. Post-1982 pennies”. Number of Pennies 5 10 15 20 25 Mass (g) Total Volume in Cylinder (ml) Actual Volume of Pennies