Chapter 1.2 Guided Notes
advertisement

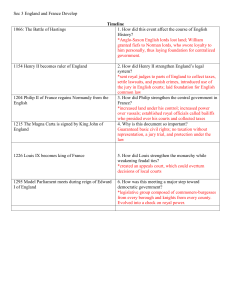
Chapter 1.2 Court System and Trial Procedure 1. As the framers wrote the constitution, some feared that the ___________ courts might threaten the ____________________ of the ____________ and the ____________________. Special Federal Courts Federal Courts State Courts U.S. Claims Court -Claims against the federal government U.S. Supreme Court (3) Each state has the following types of courts: Local Trial Courts o Speeding tickets General Trial Courts o Criminal and civil cases Juvenile Courts o Cases involving minors HIGHEST TIER U.S. Court of International Trade -Hears Civil cases concerning tariffs and import taxes U.S. Tax Court U.S. Court of Appeals (2) MIDDLE TIER -Hears cases dealing with tax laws Territorial Courts Intermediate Appellate Courts o Cases being appealed State Supreme Court -Hears cases dealing with territorial and federal law in the territories of the United States U.S. District Courts (1) LOWEST TIER STATE CASE EXAMPLES A crime that is a violation of state law. Most criminal activity falls in this category, such as robbery, assault, murder, and many drug-related crimes. Court of Military Appeals -Hears appeals of court martials FEDERAL CASE EXAMPLES • • • A controversy arising out of the state constitution or other state laws. • A case in which the state is a party, such as state tax violations. • Most real estate cases, malpractice, personal injury cases, and contract disputes. • All family, divorce, custody, inheritance and probate (will) cases. Most traffic and juvenile cases. • Cases in which the United States is a party Cases involving violations of the U.S. Constitution or federal laws Cases between citizens of different states if the amount in controversy exceeds $75,000 Bankruptcy, Copyright, Patent, and Maritime (sea) law cases. Bank Robbery in which the FDIC insures the bank Bringing illegal drugs into country or across state line Crimes committed on federal property: national parks or military reservations. Federal Court System 1. Define JurisdictionFEDERAL COURTS JURISDICTIONS TYPES OF CASES D_________________ Courts O__________________________ __________________________ Court of A_______________ A__________________________ __________________________ STATE COURTS JURISDICTIONS TYPES OF CASES L_________________________ L__________________________ __________________________ G_________________________ G_________________________ __________________________ J___________________________ S__________________________ __________________________ State Court System OTHER S__________________________ TYPES OF CASES E__________________________ __________________________ JUVENILE COURTS Juvenile Court does not refer to the place a court proceeding takes place. Instead….. Identify some differences between an adult and a juvenile: Substantive Vs. Procedural Law 1. Define Substantive Law2. Define Procedural Law- 2 types of Procedural Law 1. Criminal2. Civil- Litigation 1. Litigation2. Reasons for Litigation a. Wrongful Deathb. Survival Statute 3. Why are Statues of limitation passed? Alternative Dispute Resolution 1. Define ADRa. Mediation- b. Arbitration- c. Conciliation- d. Negotiation- Civil Law Procedure 1. What are pleadings? 2. Name the two types of pleading. Identify who files each type of pleading. 3. Below are the steps of a civil case procedure. Put the below steps in order from 1 to 7. With a 1 being the step that happens first, and a 7 being the step that happens last. _____Plaintiff files a reply _____Defendant files an answer _____Clerk of Court Issues a summons _____Plaintiff files a complaint _____Complaint is filed with the clerk of the court _____Answer is filed with the clerk of court _____Process Server issues a summons 4. Identify the 5 Methods of Discovery 5. Only Criminal cases can have a jury. a. True b. False Criminal Law Steps in a Trial Step 1: Selecting the Jury 1. Identify 2 reasons why a person may be dismissed from being a juror in a court case. 1. 2. 2 Challenges exist that allow lawyers to dismiss jurors from serving in a trial. 2. Identify the difference between peremptory challenge and challenge for a cause: a. peremptory challenge- b. challenge for a cause- Step 2: Arguments and Evidence 3. After jury members are chosen, lawyers make __________________________________. 4. What do opening statements explain? 5. Who gives their opening statement first? 6. Why do defense lawyers cross-examine the plaintiff’s witnesses? 7. What are closing arguments? Step 3: Instruction to the Jury 8. What is jury instruction? Step 4: Verdict and Judgment 9. What is a verdict? 10. What does a judgment reveal? Step 5: Remedies 11. What are the two types of remedies provided by the court? Step 6: Execution Of Judgment 12. When is a judgment enforced? Criminal Trial Procedure 1. When do criminal cases start? 2. What is due process of law? 3. Why does the law require a court hearing right away? Rights of the Defendant 4. What do “Miranda” rights tell a person? 5. What rights are stated when a person is read their “Miranda” rights? 6. A police officer may arrest a person at any time if they have a ________________________. 7. When may a police officer search a person without a warrant? 8. Who determines bail for a person who has been arrested? 9. What is probable cause? Grand Jury 10. What is an indictment? Arraignment 11. What happens if a person pleads guilty? 12. What happens if a person pleads not guilty? 13. What is a plea agreement? The Trial 14. The _______________ must be __________________ in a criminal court case. 15. When a jury cannot unanimously agree on a verdict it is called a ___________________ jury. 16. Who has the option of having a mistrial? 17. What happens if the defendant is found not guilty? 18. What happens if the defendant is found guilty? 19. What does the term “beyond all reasonable doubt” mean? Sentencing Fines- Imprisonment- Death Penalty- 3 Steps in a Juvenile Court 1. Detention Hearing- 2. Adjudicatory Hearing- 3. Disposition Hearing-