Civics: Chapter 15 - Duplin County Schools
advertisement

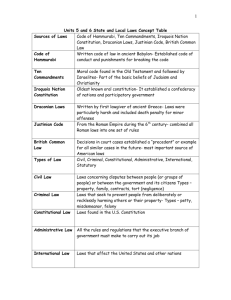
Civics: Chapter 15- Legal Rights and Responsibilities and Chapter 16-Civil and Criminal Law Study Guide Chapter 15, Section 1 (pg. 427-429) 1. What are the four characteristics that make a law a good law? Fair, reasonable, understandable, enforceable. 2. What was the first known system of written law? Code of Hammurabi 3. What was an early law code that set forth moral rules of the ancient Hebrews? 10 Commandments 4. What was the Justinian Code? Revised the Roman Laws into a more condensed set of laws- “punishment must fit the crime” 5. What was the Napoleonic code? Laws of what US state are based on this code? Updated the Justinian Code- “Louisana” Chapter 15, Section 2 (pg. 431-434) 1. What is meant by the adversary system of American courts? Explains the court room. 2. What is the difference between felonies and misdemeanors? (F) more serious crime; rape, murder 1 year or more in prison-death (NC Supereior). (M) less serios crime: vandalism 1 year or less in jail (NC District) 3. What is the difference between criminal law and civil law? Criminal- law has been broken – someone has committed a wrong doing. Civil- a legal dispute between people or over property. 4. Explain tort law. Branch of Civil law where someone acted careless and negligent. 5. What is constitutional law? Dealing with the Consitutoin 6. What is administrative law? Dealing with the executive agencies CIA, CDC, FDA, FCC, FEMA 7. What is statutory law? A law written by the legislature Chapter 15, Section 3 (pg. 436-440) 1. What is stated in the equal-protection clause in the 14th Amendment? All people are EQUAL 2. What does the 4th Amendment protect citizens against? No unreasonable searches. 3. What did the Supreme Court rule in Mapp v. Ohio? No warrant = No search. Any evidence obtained illegally can not be used against you in court – Exclusionary Rule 4. What protections does the 5th Amendment provide for people accused of crimes? Double Jeopardy, Due Process, Eminent Domain, I plead the fifth, Miranda Rights 5. What did the Supreme Court rule in Miranda v. Arizona? Suspect must be read their rights when arrested. 6. What rights does the 6th Amendment grant an accused person? Right to an attorney and jury trial 7. What did the Supreme Court rule in Gideon v. Wainwright? Right to an attorney 8. What is a bench trial? Defendant waves right to a jury and is heard by a judge only 9. What two things does the 8th Amendment outlaw? No excessive bail and no cruel an unusual punishment 10. What did the Supreme Court rule in Furman v. Georgia? Death Penalty was cruel and unsuaual as it was being applied Chapter 16, Section 1 (pg. 449-451) 1. What is the first step in a civil case? Plaintiffs attorney files a complaint with the court- lists the issues and names the defendant(s) 2. What happens in the discovery phase of a trial? Lawyers gather facts and question both sides. 3. Why do some defendants offer settlements in lawsuits? They see they have a weak case and will likely lose. This is a way to save $. 4. What is the difference between mediation and arbitration? Mediation- third party (neutral) gives a non legally binding settlement (parties do NOT have to take). Arbitration- third party, acts more like a judge, gives a legally binding agreement (parties have to accept) 5. What is meant by a “preponderance of evidence” in a civil trial? Plaintiff’s attorney must prove the defendant guilty with a “presponderence of evidence” more likely then not they are responsible. 6. What happens in a civil case if the plaintiff wins? What happens if the defendant wins? (P) winsprecedent/ruling is set. (D) plaintiff pays for all court cost 7. If the losing side is not happy with the outcome of the trial, what action can they take? Appeal to a higher court to review lower courts decision Chapter 16, Section 2 (pg. 453-458) 1. What does a state’s penal code state? OMIT 2. Why are some crimes considered “victimless crimes”? They do not hurt anyone or pose danger gambling 3. What are some rights citizens convicted of felonies may lose? Voting, Owning guns, Jobs 4. When do criminal cases begin? At the arrest 5. What is an indictment? Formal charge of a crime 6. What occurs at the arraignment? Defendant enters a plea: guilty/not guilty 7. What is the standard of guilt in a criminal trial? Burden of Proof lies with the Prosecution they must prove the defendant is guilty “BEYOND A REASONABLE DOUBT” 8. What happens if the jury cannot agree on a verdict? Declares a mistrial HUNG JURY Chapter 16, Section 3 (pg. 461-463) 1. What is the primary goal of juvenile courts? Rehabilitatin 2. What is the difference between the neglect and delinquency cases heard in juvenile court? Neglect- child abuse and delinquency- they have commited a crime. 3. What are the differences between juvenile trials and adult trials? Juveniles- no public trial, no jury, no photographs or finger prints. 4. What rules did the Supreme Court establish for juvenile criminal cases? (In re Gault case) Juvey’s have similar rights as adults