lecture 15
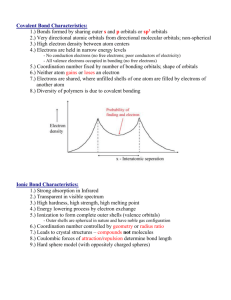
advertisement

What’s coming up???
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Oct 25
Oct 27
Oct 29
Nov 1
Nov 3,5
Nov 8,10
Nov 12
Nov 15
Nov 17
Nov 19
Nov 22
Nov 24
The atmosphere, part 1
Midterm … No lecture
The atmosphere, part 2
Light, blackbodies, Bohr
Postulates of QM, p-in-a-box
Hydrogen and multi – e atoms
Multi-electron atoms
Periodic properties
Periodic properties
Valence-bond; Lewis structures
VSEPR
Hybrid orbitals; VSEPR
Ch. 8
• Nov 26
Hybrid orbitals; MO theory
Ch. 12
•
•
•
MO theory
bonding wrapup
Review for exam
Ch. 12
Ch. 11,12
Nov 29
Dec 1
Dec 2
Ch. 8
Ch. 9
Ch. 9
Ch. 9
Ch.9,10
Ch. 10
Ch. 10
Ch. 11
Ch. 11
Ch. 11, 12
Describing the bonding in more complicated
molecules…...
PROPYNE: CH3CCH 16 valence electrons
Lewis Dot Structure…..
H
H
C
C
C
H
H
CENTRAL CARBON NEEDS OCTET
PROPYNE: CH3CCH has the structure
H
H
C
C
C
H
Tetrahedral Carbon:
Hybridization?
sp3
H
Linear Carbons
Hybridization?
sp
PROPYNE: CH3CCH has the bonding
H
H
C sp3
overlaps
with H 1s
s bond
C
H
C
C
H
C p overlaps with C p
p bonds
C sp overlaps with C sp
C sp3 overlaps with C sp s bond
s bond
H
These four
atoms are in a
straight line
C
C
C
H
H
H
FREE
ROTATION
of Methyl
Group.
LACTIC ACID
The bonding frame work of lactic acid
H
H
H
C
C
H
O
H
O
C
O
H
QUESTION
H
O
H
H
C
C
C
O
THE BOND ANGLE
SHOWN IS
H
H
1
120°
2
90°
3
4
180°
109°
O
H
QUESTION
H
H
H
C
C
H
O
O
C
O
THE BOND ANGLE
SHOWN IS
1
H 2
3
4
120°
90°
180°
109°
H
QUESTION
H
H
H
C
C
H
O
C
O
THE BOND ANGLE
SHOWN IS
O
1
H 2
3
4
109°
90°
120°
180°
H
LACTIC ACID
O
O
H
H
C
H
O
C
C
H
H
H
OK, so we have it all figured out!
… or do we??
Let’s think about oxygen, O2
12 electrons … Lewis picture gives
:O::O:
.. ..
3 electron groups around each …
sp2 and 1200
O
s bond
O
p bond
All electrons paired … diamagnetic
BUT O2 is paramagnetic unpaired electrons!!
MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
Atoms, molecules or ions with at least one
unpaired electron are paramagnetic.
Paramagnetic materials are strongly attracted
to magnetic fields.
Nitrogen atom is PARAMAGNETIC
1s
N
1s22s22p3
2s
2p
Let’s try another approach …
Combining the two 1S orbitals from two hydrogen atoms
will give another way to think about bonding
COMBINATION OF ORBITALS
Remember, when we take linear combinations
of orbitals we get out as many as we put in.
Here, the sum of the 2 orbitals
1sA + 1sB = MO1
builds up electron density between nuclei.
90% probability
COMBINATION OF ORBITALS
1sA – 1sB = MO2
results in low electron density between nuclei
1sA + 1sB = MO1
builds up electron density between nuclei.
THE MO’s FORMED BY TWO 1s
ORBITALS
ANTI-BONDING
s1s*
1sA – 1sB = MO2
BONDING
Each orbital
can hold up to
two electrons.
s1s
1sA + 1sB = MO1
COMBINING TWO 1s ORBITALS
E
Energy of a
1s orbital in
a free atom
A
B
Energy of
a 1s orbital
in a free
atom
COMBINING TWO 1s ORBITALS
E
Energy of a
1s orbital in
a free atom
A
B
s1s
Energy of
a 1s orbital
in a free
atom
Energy of 1sA+1sB MO
ADDITION gives an
Energy more negative than average of original orbitals
SUBTRACTION gives an….
Energy more positive than average of original orbitals
E
Energy of a
1s orbital in
a free atom
A
s1s*
s1s
B
Energy of
a 1s orbital
in a free
atom
ADDITION gives an….
Energy more negative than average of original orbitals
COMBINING TWO 1s ORBITALS
s1s*
E
1sA
A
B
s1s
1sB
The bonding in H2
H
H2
H
s1s*
E
1s
1s
s1s
H
H2
H
s1s*
E
1s
1s
s1s
H2: (s1s)2
He2
Atomic configuration of He
He
He2
He
s1s*
E
1s
1s
s1s
One pair of electrons goes in s1s
and the next pair in
s1s*
1s2
He2: (s1s)2(s1s*)2
The He2 molecule is not
a stable species.
He
He2
He
s1s*
E
1s
1s
s1s
The bonding effect of the (s1s)2 is cancelled by the
antibonding effect of (s1s*)2
BOND ORDER
Useful concept:
The net number of bonds existing after the
cancellation of bonds by antibonds.
In He2 the electronic configuration is….
(s1s)2(s1s*)2
the two bonding electrons were cancelled out
by the two antibonding electrons.
There is no BOND!
BOND ORDER = 0
BOND ORDER
A measure of bond strength and molecular stability.
If # of bonding electrons > # of antibonding electrons
the molecule is predicted to be stable
Bond
order
= 1/2 {
= 1/2 (n
# of bonding
# of antibonding
–
electrons(nb)
electrons (na)
b
- na)
A high bond order indicates high bond
energy and short bond length.
Consider H2+,H2,He2+,He2……….
}
First row diatomic molecules and ions
H2
H2+
He2+
He2
Magnetism
Dia-
Para-
Para-
—
Bond order
1
½
½
0
Bond energy
(kJ/mol)
436
225
251
—
Bond length
(pm)
74
106
108
—
s1s*
E
s1s