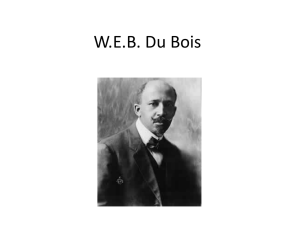required segregation in
advertisement

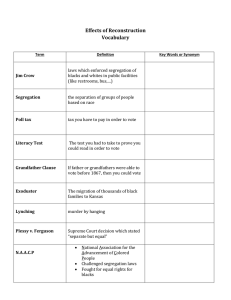
Slavery to Civil Rights Part 2 Jim Crow Laws Southern states passed laws requiring segregation 1890’s song sheet Life Under Jim Crow • Beginning in the 1880’s Southern states and cities began passing laws requiring racial segregation • separate train cars for blacks and whites (challenged later in Plessy) Also: required segregation in: hotels restaurants parks and every facility open to the public Atlanta even required separate Bibles to swear on for blacks & whites Plessy v. Ferguson - 1896 Can separate really ever be equal? Booker T. Washington • son of enslaved parents • hired by the state of Alabama in 1881 to run Tuskegee Institute (vocational school) • farming, forestry, plumbing, sewing, nursing • believed blacks could achieve economic prosperity, independence, and respect of whites by succeeding in these fields • urged blacks to give in to white racism and not challenge Jim Crow laws (accommodation) • many agreed, saw economic rights as being more important than winning the vote W.E.B. Du Bois • opposed to Washington’s meek acceptance of humiliating discrimination • born in 1868, raised in a free family in Mass. • 1st African American to receive a Ph.D. from Harvard, taught history and social science at Atlanta University • founded the NAACP in 1909 • called for blacks to demand equality at once • key to equality was the vote… not economic • with the vote would come political power to end lynching, provide better schools for children, challenge white domination of society What about the North? de facto segregation Jackie Robinson 1947 Supreme Court Decisions in 1950 • RR dining cars in South must provide equal service • black students couldn’t be segregated within a school • “intangible factors” had to be considered (not just buildings and books Brown v. Board of Education Linda Brown Chief Justice Earl Warren “We conclude that in the field of public education the doctrine of “separate but equal” has no place. Separate educational facilities are inherently unequal” Unanimous Decision on May 4th 1954 What does the following saying mean to you? “a picture is worth a thousand words” "African Americans and White Americans have faced similar problems when wanting to participate in politics." Defender (Chicago) June 12, 1954 by J. Kennedy Democrat (Arkansas) May 22, 1954 “Let That One Go. He Says He Don’t Wanna Be Mah Equal.” by Bill Maudlin March 2, 1960 “Inch by Inch” by Bill Mauldin September 1, 1960 “I’m Eight….” by Herblock May 17, 1962 “…One Nation…Indivisible...” by Herblock ca. 1977 Southern Manifesto Signed by 100 members of Congress “to resist forced integration by any means” “ I don’t believe you can change the hearts of men with laws or decisions.” President Dwight D. Eisenhower Resistance to Brown Southern states passed more than 450 laws aimed at preventing enforcement of the Brown decision The Montgomery Bus Boycott December 1, 1955 Crisis at Little Rock Arkansas 5 days after the Brown decision Martin Luther King The SCLC • Southern Christian Leadership Conference Nonviolent Resistance Sit-Ins The SNCC • The Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee • Civil Disobedience “ jail, not bail” Kennedy Courted the Black Vote He endorsed sit-ins Promised a civil rights bill MLK’s Arrest • sit-in in Atlanta department store • ruled violation of probation for driving without a license • sentenced to four months of hard labor on Georgia chain gang • JFK an RFK intervened on King’s behalf The Freedom Riders Educating Black Voters Difficult Tests Misspelled Words Omissions SNCC (student nonviolent coordinating committee) • effective in organizing • brought violent response from white segregationists Birmingham Demonstrations “Letter From Birmingham Jail” “…For years now I have heard the word “Wait!” It rings in the ear of every Negro with piercing familiarity. This “Wait” has almost always meant “Never.” We must come to see…that “justice too long delayed is justice denied.” - Martin Luther King “Letter from Birmingham Jail,” 1963 June 11, 1963 JFK announces he will send Congress a civil rights bill that will deliver crushing blows to segregation June 11, 1963 • court order requiring the admission of two African American students University of Alabama • head of Mississippi NAACP • killed by a white sniper Medgar Evers March On Washington Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed segregation in the US schools and public places Civil Rights Act of 1968 prohibited discrimination in housing 24th Amendment prohibits conditioning the right to vote in federal elections on payment of a poll tax or other types of tax.