US History- 7.03
advertisement

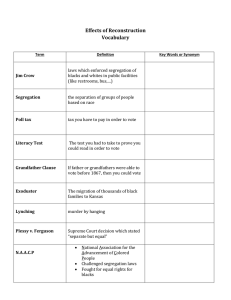
13th Amendment- Freed the slaves 14th Amendment- Due Process; everyone equal before the law and entitled to same rights 15th Amendment- Universal Male Suffrage De Jure- segregation based on law De Facto- segregation based on tradition (social and economic factors- not laws) Disenfranchisement- deny a certain group the right to vote KKK and lynchings will be a means to keep blacks from voting Jim Crow Laws- laws preventing former slaves from doing certain things Voting Restrictions Poll Tax- tax that was required in order to vote Literacy Tests- required tests to qualify for voting Grandfather Clause- people could still vote (even if they didn’t pay tax or pass test) if their father or grandfather was eligible to vote before Jan. 1, 1867 Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) Separation by race was legal and did not violate the 14th amendment “Separate but equal” was constitutional Ida Wells Journalist- investigated and spoke publicly on lynching Co-founded the National Association of Colored Women Fought for civil rights, especially after Plessy decision Booker T. Washington Born into slavery, educated after emancipation Became head of Tuskegee Normal and Industrial Institute Wanted whites and blacks to work together for social progress Wanted economic independence for black Americans Preached evolution and integration, not revolution Did not oppose segregation Challenged by Ida Wells and W.E.B. DuBois W.E.B. DuBois Disagreed with Washington Believed blacks should be politically, legally and socially active to become truly equal Niagara Movementmeeting of leading African-Americans that led to the founding of the NAACP (National Association for the Advancement of Colored People) Washington •Preached accomodation (for now)- accept segregation •Blacks better themselves thru hard work and education- economic opportunities DuBois •Advocated political action and a civil rights agenda •Co-founder of NAACP •Want immediate end to segregation •Achieve end to segregation by fighting it politically- use court system “Back to Africa Movement” Move back go Africa to find homeland Important for building “Black Pride” Great Migration Movement of thousands of African-Americans to northern cities in search of jobs Lead to an increase in de facto segregation in urban cities (NYC, Philadelphia, Chicago, Detroit, etc.) African Americans thought North would be better- ability to open small businesses, buy or rent property, send their children to public school Discrimination still exists in North