PATTERNS OF CIRCULATION
advertisement
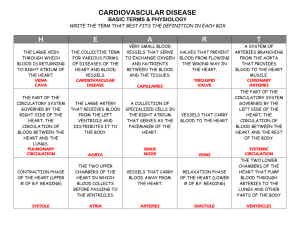
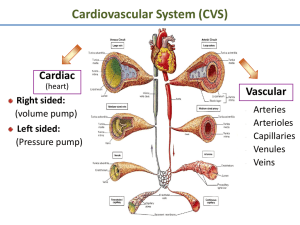
PATTERNS OF CIRCULATION Blood moves through the body in a continuous pathway, of which there are TWO MAJOR PATHS; THE PULMONARY AND SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION. THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION • CARRIES BLOOD BETWEEN THE HEART AND THE LUNGS. THIS CIRCULATION BEGINS AT THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND ENDS AT THE LEFT ATRIUM • 3. Oxygen-Poor blood is pumped out of the Right Ventricle of the Heart into the Lungs through the Pulmonary Arteries. These are the only Arteries in the Body to Carry Deoxygenated Blood. • 4. Blood returns to the Heart through the Pulmonary Veins, the only Veins to carry oxygenrich blood. • 5. THE LUNGS ARE THE ONLY ORGANS DIRECTLY CONNECTED TO BOTH CHAMBERS OF THE HEART. THE SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION • STARTS AT THE LEFT VENTRICLE AND ENDS AT THE ATRIUM, CARRIES BLOOD TO THE REST OF THE BODY. • 7. Oxygen-rich blood leaving the Heart passes through the Aorta and into a number of Arteries that supply blood to every part of the body. • 8. SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION SUPPLIES EACH MAJOR ORGAN WITH BLOOD, INCLUDING THE HEART. • 9. The Heart receives its supply of Blood from a PAIR of CORONARY ARTERIES leading from the Aorta. Blood enters into Capillaries that lead to Veins through which blood returns to the Right Atrium. The Systemic System can be divided into THREE SUBSYSTEMS: • A. CORONARY CIRCULATION - SUPPLIES BLOOD TO THE HEART. • B. RENAL CIRCULATION - SUPPLIES BLOOD TO THE KIDNEYS. Nearly one-forth of the blood that is pump into the Aorta by the Left Ventricle flows to the Kidneys. The Kidneys Filter Waste From the Blood. • C. HEPATIC PORTAL CIRCULATION - Nutrients are picked up by capillaries in the small intestines and are transported to the Liver. Excess nutrients are stored in the Live for future needs. The Liver receives oxygenated blood from a large Artery that branches of the Aorta.