Chapter 37 Notes Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
advertisement

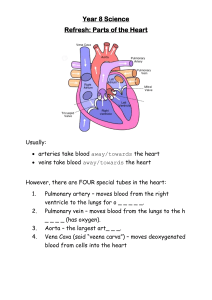
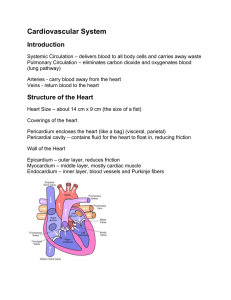
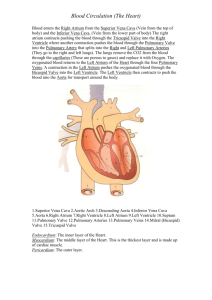
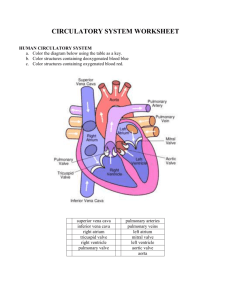
37-1 Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, a series of blood vessels, and the blood that flows through them. Structures of the heart that you should knowSuperior Vena Cava, Pulmonary Veins, Pulmonary Valve, Tricuspid Valve, Inferior Vena Cava, Aorta, Pulmonary Arteries, Left Atrium, Right Atrium, Left Ventricle, Right Ventricle, Mitral Valve, Myocardium, Pacemaker (or SA node). Pulmonary circulation is circulation of blood through the heart and lungs. Systemic circulation is the oxygen rich blood flows into the left side of the heart and then is pumped to the rest of the body. Blood vessels-The large blood vessel (pumping blood from the left ventricle) is the Aorta. There are 3 types of blood vessels-arteries, capillaries and veins. How many times does your heart beat in one minute. Please find your pulse and count the beats for one minute. _____beats per minute. “Normal” is _____per minute. Diseases of the Circulatory SystemAtherosclerosis is a condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries. High Blood pressure(hypertension) When the heart contracts, it produces a wave of fluid pressure in the arteries. This force is known as blood pressure. As the heart relaxes, blood pressure decreases. Through sensory receptors in several places of the body, your body regulates blood pressure by detecting different levels and sending impulses to the medulla oblongata region of the brain stem. Normal blood pressure measures at 80/120. Blood pressure needs to be checked with a bp cuff. Body contains4-6 liters of blood. This is about 8% of the total mass of the body. Plasma makes up about 55% of the blood. Hemoglobin is the ironcontaining protein that binds to oxygen in the lungs and then transports it to the tissues throughout the body where to oxygen is released. Draw, Label and Explain (2-4 sentences each). Figure 37-3 Page 945 Figure 37-6 Page947 The basic function performed by the human respiratory system is to exchange oxygen and CO2. The pharynx is a passageway for both air and food. Air moves from the pharynx into the trachea. The epiglottis covers the entrance to the trachea. Count your breaths per minute. How many times did you breath in one minute??____per minute. Blood Transfusions page 954. Answer all questions. Draw, label and explain Figure 37-11 Answer Questions 1-23 on page 954 Due-5-22-13 As a result of coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable(homeostatic), despite changes in the outside environment. Essential Question- What system is important for O2 and Co2 exchange. Where does the exchange take place?