APHY 102 Review Guide for Comprehensive Final Chapter 15
advertisement

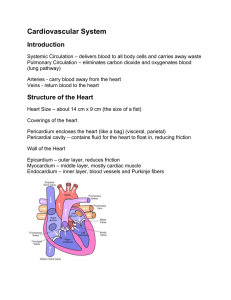
APHY 102 Review Guide for Comprehensive Final Chapter 15- Cardiovascular System I. Heart Anatomy a. Pericardium – covers the heart b. Chambers i. Right Atrium – receives blood from body ii. Left Atrium – receives blood from lungs iii. Right Ventricle – pumps blood towards lungs iv. Left Ventricl – pumps blood towards body c. Great Vessels i. Superior & Inferior Vena Cava – returns blood to right atrium ii. Pulmonary Trunk (Arteries) – Conveys blood from right ventricle to lungs iii. Pulmonary Veins – returns oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium iv. Aorta – Conveys blood from left ventricle to body d. Valves i. Atrioventricular Valves – between atria and ventricles 1. Tricuspid – guards right AV orifice 2. Bicuspid –guards left AV orifice ii. Semilunar Valves – guard pulmonary arteries and aorta 1. Pulmonary valve – guards pulmonary trunk 2. Aortic valve – guards aorta e. Pathway of blood through heart Vena Cava → right atrium→ tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary trunk → Pulmonary Arteries → Lungs → Pulmonary Veins → Left Atrium → Bicuspid Valve → Left Ventricle → Aorta II. Blood Vessels a. Walls of blood vessels i. Tunica Externa (outer) – connective tissue ii. Tunica Media (middle) – smooth muscle fibers 1. Vasoconstriction – muscles contract & decrease diameter of vessel 2. Vasodilation – muscles relax & diameter of vessel increases iii. Tunica Interna (inner) – endothelium (smooth squamous cells) b. Types of vessels i. Artery – conveys blood away from heart ii. Vein – conveys blood towards the heart iii. Capillaries – smallest blood vessels, where gas, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged c. Factors of Venous Return 1. Low blood pressure in veins: Respiratory movements, skeletal muscle contractions, valves, and vasoconstriction return blood towards heart d. Systemic Circulation i. Aorta 1. Ascending Aorta 2. Aortic Arch 3. Descending Aorta a. Thoracic Aorta b. Abdominal Aorta ii. Arteries to brain 1. Internal Carotid Arteries – 75% of blood to brain 2. Vertebral Arteries – 25% of blood to brain 3. Circle of Willis – anastomes of internal carotid and vertebral arteries iii. Abdominal Branches 1. Celiac trunk – supplies stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver 2. Renal Arteries – supplies kidneys 3. Hepatic Portal Vein- nutrient rich blood from abdominal viscera to liver Chapter 14 – Blood I. Components a. Plasma i. Water ii. Electrolytes and nutrients iii. Plasma Proteins b. Formed Elements i. Red Blood Cells – erythrocytes ii. White Blood Cells – leukocytes iii. Platelets –thrombocytes c. Red Blood Cells i. Characteristics 1. Anucleated 2. 1/3 volume is hemoglobin (transports Oxygen) 3. Biconcave ii. Formation 1. Formed in red bone marrow 2. Erythropoietin a. hormone stimulates RBC formation b. Secreted by kidneys iii. Destruction 1. RBCs destroyed by liver or spleen d. White Blood Cells i. Neutrophil – phagocytize bacteria ii. Eosinophil – attacks parasitic worms iii. Basophils – secrete heparin and histamine iv. Monocytes – macrophages v. Lymphocytes – immunity e. Platelets i. Cell fragments ii. Formation of blood clots f. Hemostasis i. Stoppage of bleeding ii. 3 major events 1. Vasospasm 2. Platelet plug formation 3. Blood coagulation – formation of blood clot Chapter 13 – Endocrine System I. Hormone a. Secreted into blood stream b. Act on distant target cells II. Major Endocrine Glands a. Thyroid Gland i. T3 & T4 1. Increases rate of metabolism 2. Determines calories for basal metabolic rate ii. Calcitonin 1. Secreted by C-cells 2. Lowers blood calcium through bone deposition a. Stimulates osteoblasts and inhibits osteoclasts b. Parathyroid Glands i. Parathyroid Hormone- Increases blood calcium levels through bone resorption c. Adrenal Medulla i. Epinephrine & Norepinephrine - Fight or Flight Response d. Adrenal Cortex i. Aldosterone – sodium reabsorption ii. Cortisol – Increases glucose levels in blood e. Pancreas i. Glucagon – raises blood glucose levels (between meals) ii. Insulin – lowers blood glucose levels (following a meal) f. Posterior Pituitary Gland i. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) – water reabsorption ii. Oxytocin – uterine contractions g. Anterior Pituitary Gland i. Growth Hormone – Cell growth and division ii. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone – stimulates thyroid gland Chapter 16 – Lymphatic System & Immunity I. Lymphatic Vessels a. Returns excess fluid to blood circulation b. Thoracic Duct – drains lymph from lower body and left upper body c. Right Collecting Duct – drains lymph from right upper body II. Lymph Nodes a. House Lymphocytes ( B-cells and T-cells) b. Filters lymph c. Located in groups (cervical, axillary, inguinal, ect.) III. Spleen a. Located in upper left abdominal quadrant b. Filters blood, removes old RBCs, houses lymphocytes IV. Thymus a. Shrinks (atrophies) with age b. Houses T-cells c. Secretes Thymosin – promotes T-cell maturation Immunity a. Innate i. Mechanical Barrier – skin, mucous, tears ii. Chemical Barrier – tears, mucus, HCl in stomach iii. Cellular defense – phagocytosis V. b. Adaptive i. Recognizes, responds, and remembers a threat ii. Antigen/Antibody interaction iii. Antibody-mediated immunity – B cells secrete antibodies iv. Cell-mediated immunity – T cells attack directly Chapter 17 – Digestive System I. Alimentary Canal a. Extends from mouth to anus b. Accessory glands secrete juices into canal - Liver, Gall Bladder, Pancreas c. Movements – segmentation and peristalsis II. Mouth a. b. c. d. Mastication – chewing food Bolus – food + saliva Deglutition – swallowing Teeth i. Types 1. 8 incisors – cutting 2. 4 canines – tearing 3. 8 bicuspids – grinding 4. 12 molars – grinding ii. Structure 1. Enamel – hardest substance in body 2. Dentin – living tissue 3. Pulp –connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves III. IV. V. Stomach a. Mixes food with gastric juices = chyme b. Very little absorption c. Gastric Glands i. Chief cells – secrete pepsinogen ii. Parietal cells secrete Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) 1. HCL + Pepsinogen → Pepsin (digests proteins) iii. Mucous cells secrete mucus Pancreas a. Acinar Cells secrete pancreatic juice b. Enzymes: i. Amylase – digests carbohydrates ii. Lipase – digests lipids iii. Nucleases – digests nucleic acids iv. Trypsin – digests proteins Liver a. Location: upper right abdominal quadrant b. Lobule – functional unit of liver i. Hepatocytes – liver cells VI. VII. c. Functions of liver i. Forms bile – emulsifies fats ii. Synthesizes proteins iii. Destroys old RBC iv. Synthesizes glycogen from glucose v. Removes bacteria from blood Small Intestine a. Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum b. Absorbs nutrients and water Large Intestine a. Absorbs water and forms feces b. Houses intestinal flora = bacteria Chapter 19 – respiratory system I. Events a. Ventilation – movement of air into and out of lungs b. Cell Respiration – cells use Oxygen for ATP synthesis, CO2 is produced as waste II. Upper Respiratory Tract a. Nasal Cavity i. Warms the air ii. Moistens the air iii. Filters the air iv. Smell b. Larynx i. Houses vocal cords ii. Epiglottis – covers glottis when swallowing c. Trachea i. 20 “C” shaped rings of hyaline cartilage ii. Lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia and goblet cells 1. Goblet cells – secrete mucus to trap debris 2. Cilia – remove debris from airway d. Lungs i. ii. iii. iv. Alveoli – simple squamous epithelium for gas exchange Surfactant – reduces surface tension between alveoli Right lung = 3 lobes, left lung = 2 lobes Pleura = membrane surrounding lungs e. Control of breathing i. Medulla Oblongata –primary respiratory centers for control of breathing Chapter 20 – Urinary System I. Kidneys a. Location i. Behind peritoneal membrane – retroperitoneal b. Functions i. Produces urine ii. Regulates blood pressure iii. Regulates pH c. Blood Supply i. Renal Arteries d. Structure i. Hilum = entrance ii. Renal Capsule = fibrous C.T. iii. Renal Medulla iv. Renal Cortex II. Nephron a. Functional unit of kidneys b. Renal Corpuscle – site of filtration i. Glomerulus = ball of capillaries ii. Glomerular Capsule c. Renal Tubules – site of reabsorption and secretion i. Proximal Convoluted Tubule ii. Descending Nephron Loop iii. Ascending Nephron Loop iv. Distal Convoluted Tubule d. Glomerular Filtrate i. 180Liters formed per day ii. 99% is reabsorbed, 1% is excreted as urine iii. Water is reabsorbed by osmosis III. Ureters a. Convey urine from kidneys towards urinary bladder b. Passes urine by Peristalsis IV. Urinary Bladder a. Detrusor muscle – bulk of urinary bladder b. Transitional epithelium – lines urinary bladder, allows for distension V. Urethra a. Conveys urine to environment b. Female = 1.5 inches c. Male = 7.5 inches i. Prostatic Urethra – joins prostate gland ii. Membranous Urethra- External Urethral Sphincter iii. Penile Urethra- through penis Chapter 21 – Water and Electrolyte Balance I. Distribution of water a. Intracellular Fluids i. Enclosed by membrane ii. Contains 60% of total water volume b. Extracellular Fluids i. Contains 40% of total water volume ii. Plasma, interstitial fluids, lymph, synovial fluid, serous fluid, CSF II. Distribution of Electrolytes a. Sodium – primary cation in extracellular fluid b. Potassium – primary cation in intracellular fluid III. Movement of fluids a. Hydrostatic Pressure b. Osmosis i. Hypotonic ECF with over hydration – water enters cell and cell swells ii. Hypertonic ECF with dehydration – water leaves cell and cell shrinks IV. Regulation of water intake and output a. Thirst Mechanism – within hypothalamus i. Stimulates thirst sensation ii. Sensation is inhibited when the stomach is distended from drinking fluids V. b. Osmoreceptor-ADH Mechanism- within hypothalamus i. With water loss, osmoreceptors in hypothalamus stimulate ADH secretion from Posterior Pituitary Gland ii. ADH increases water reabsorption in kidneys iii. Urine output decreases Buffers a. Buffer – resists changes in pH b. Blood pH 7.35-7.45 c. Buffers in Blood i. Bicarbonate ii. Phosphate iii. Proteins – most important protein buffer is hemoglobin VI. Respiratory excretion of CO2 a. CO2 lowers the blood pH (increases acidity) b. Accumulation of CO2 increases rate of respiration c. Expiration of CO2 from lungs removes excess CO2 VII. Renal Secretion of H+ a. Kidneys regulate blood pH by secreting H+ into the renal tubules