study question 2
advertisement

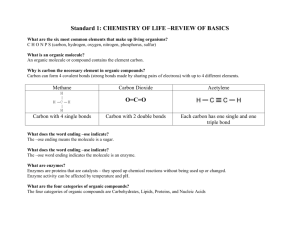
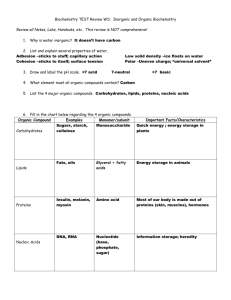
Organic Chemistry. Standard 10. Ms. Siddall. Standard 10a: Large molecules Organic chemistry = The study of organic compounds, which are compounds containing carbon. There are over 16 million carbon compounds! study question 1 Which compounds are organic? C3H8 Al2O3 SO2 C2H5O Organic molecules Hydrocarbon: An organic molecule composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms. Example: gasoline, methane. study question 2 Which compounds are hydrocarbons? C3H8 Ca(OH)2 NO2 C22H46 Polymer A large organic molecule consisting of repeating units called monomers. Example: plastic, protein. H H Plastic Monomer H C C H H H H H H H H H H H Polymer C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H Polymer: Starch Starch = polysaccharide (polymer) sugar molecule = monomer study question 3 What is a polymer? Give an example. Standard 10b: carbon bonding characteristics Carbon: A unique atom 4 valence electrons forms 4 bonds. forms over 16 million compounds….. • •C• • electrons study question 4 Why is carbon a unique atom? Carbon: e.x. Methane (CH4) Four single covalent bonds: Shape = tetrahedral. H H C H H 2 electrons = 1 bond Carbon: e.x. Formaldehyde (CH2O). One double covalent bond: Shape = trigonal planar. H H C 4 electrons = 2 bonds = double bond O Carbon: e.x. Carbon dioxide (CO2) two double covalent bonds Shape = linear. O C O Carbon: e.x. Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) One triple covalent bond Shape = linear H C N study question 5 What is the shape of methanone (CH2O)? O H C H Standard 10c: amino acids & proteins Amino Acids: Proteins are polymers Amino acids are monomers combine with peptide bond. (polypeptide) One molecule of water is produced when a peptide bond is formed (= dehydration) Unique function of amino acids and proteins depends on shape and properties. Example: cysteine, glutamine, and glycine combine to remove toxins from the body. cystein Glycine Glutamine study question 6 What are the monomers that make up proteins? DNA Polymer Formed from nucleic acids (monomers) Contains ‘phosphate backbone’ (= bonds) hydrogen bonds connect strands to form a double helix DNA contains the ‘blueprint’ for building proteins study question 7 What is DNA made up of? Naming organic compounds. Carbons 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Root name Meth Eth Prop But Pent Hex Hept Oct Non Dec ending Single bond -ane Double bond -ene Triple bond -yne Examples: H • Methane H C H H H H • Ethane H C C H H H H H H • Propane H C C C H H H H study question 8 Name this compound: H H H H H C C C C H H H H H Examples: Name = ethane Name = ethene Name = ethyne H H H C C H H H H C C H H H H C C H study question 9 Name this compound: H H H H C C C H H Benzene ring H H H C C C H C C C H H shorthand Rules 1. Name the ‘parent’ chain (the longest chain) 2. Use number to denote bond if necessary 3. number the branch (end in –yl) and add as a prefix 2-pentene 2-methylpentane study question 10 Draw: 3-methyl hexane Propyne Copy table 23.1 from page 726. Add two extra columns for an example Omit the first and last row study question 11 What type of compound is this? H H H C C C H H H O