Species, Area, & the Equilibrium Theory of Island Biogeography
advertisement

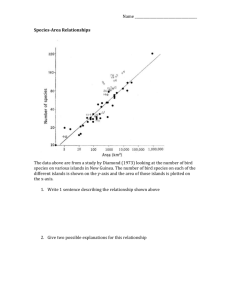
Species, Area, & the Equilibrium Theory of Island Biogeography as a foundation paradigm in conservation biology Species, Area, & the Equilibrium Theory of Island Biogeography as a foundation paradigm in conservation biology Conservation planning & design Fragmentation effects Species loss equation—predicting extinction Island models in gene flow, metapopulations, landscape ecology • Samples, within contiguous area • Isolates, islands, z high • Samples, within contiguous area, z low • Isolates, islands The Plot Thickens! Richness as a f(area, distance) % Saturation as a f (distance) Species-area relations • • • • • S = cAz z is much less than 1 log S = log c + z log A Variation in c: places and taxa Variation in z: area and isolation z = .10-.15 for samples z = .18-.35 for islands IF z = .3, 50/10 Rule Island Observations Islands have fewer species than samples within contiguous continental areas as a function of size Islands have ever fewer species as they get smaller (z is higher) Isolated islands have fewer species than less isolated islands of the same size Threat 1: Habitat Loss & Fragmentation • Area decreases (Grain decreases) • Isolation increases (Distance increases) • Fewer species expected • Insularization Occam’s principle of parsimony with a warning from Einstein One should not increase beyond what is necessary the number of entities required to explain anything William of Ockham Everything should be made as simple as possible but not simpler Albert Einstein IBT The Theory! • Immigration, extinction – Straight to concave • Turnover • Near, Far • Large, Small Immigration Rate Rate of Immigration High Low 0 Number of Species Many Extinction Rate Rate of Extinction High Low 0 Number of Species Many Equilibrium Low Rate of Extinction Rate of Immigration High Equilibrium 0 Number of Species Many Far from Mainland Number of Species Rate of Extinction Rate of Immigration Isolation Rate of Immigration Large Island Number of Species Rate of Extinction Area Small, Far Island Number of Species Rate of Extinction Rate of Immigration Equilibrium Small, Close Island Number of Species Rate of Extinction Rate of Immigration Equilibrium Large, Close Island Number of Species Rate of Extinction Rate of Immigration Equilibrium Large, Far Island Number of Species Rate of Extinction Rate of Immigration Equilibrium IBT Extensions of Theory! • Target effect • Rescue effect I E Distance MW Rescue Area Target MW Extensions of Theory! • Target effect • Rescue effect • Landscape ecology: matrix, patch quality, corridor Simberloff: Experimental Test Another kind of evidence… • Species relaxation • Faunal collapse • Insularization Conservation Lessons of Landbridge Islands The Sundra Shelf after 10,000 yrs Island Area Initial Present 1000km2 S S Borneo 751 153 123 Sumatra 425 139 117 Java 126 113 74 Bali 5 66 19 % E 20 16 35 71 Land bridge islands Barro Colorado Island, Panama 1. Hilltop = 15.7 km2 of lowland tropical forest. 2. Isolated in 1914 when Lake Gatun was formed by construction of the Panama Canal. 3. Knowing area and period of isolation, can model extinction. 4. 108 species of breeding birds in 1938. 5. Terborgh used land bridge model to predict 17 would be lost in 50 years; really 13 = 12% of 108. So why does insularization lead to species loss? The 3 Step Process of Species Loss and Extinction Debt The 3 Step Process of Species Loss and Extinction Debt Instantaneous Sampling Fast Isolation Slow Area The 3 Step Process of Species Loss and Extinction Debt Instantaneous Fast Faster & Greater Loss as Area Slow The 3 Step Process of Species Loss and Extinction Debt Instantaneous Fast Faster & Greater Loss as Area Slow The 3 Step Process of Species Loss and Extinction Debt Instantaneous Fast Faster & Greater Loss as Area Slow Extinction debt Steeper z Pattern and process (A.S. Watt 1947) O Chestnut Tree, Greatrooted blossomer Are you the leaf, the blossom, or the bole? O body swayed to music, O brightening glance How can we tell the dancer from the dance? --WB Yeats The Species Loss Equation SNOW = cANOWz SORIG = cAORIGz The Species Loss Equation SNOW / SORIG = (ANOW / AORIG ) z The Species Loss Equation SNOW / SORIG = (ANOW / AORIG ) Critique? z