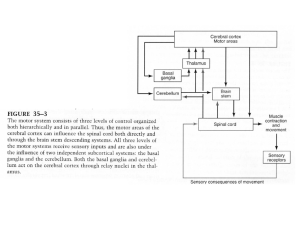
Alpha Motor Neuron

Jose Ramirez-Vasquez 1
Spinal Motor Neuron
Spinal motor neurons (sMNs) are cells in the central nervous system (CNS) (Wada et al., 2009).
These neurons can project their axons outside the CNS, and they control muscles directly or indirectly through neuromuscular junctions (Wada et al., 2009).
Contents
1 Function
2 Anatomy
2.1
Alpha motor neuron
2.2 Gamma motor neuron
3 Neurotransmitters
o 3.1 Acetylcholine
4 Physiology
5 References
Function
These neurons can project their axons outside the CNS, and they control muscles directly or indirectly through neuromuscular junctions (Wada et al., 2009).
Anatomy
Spinal motor neuron making synapse onto skeletal muscle; blue is motor neuron terminal, red is neurotransmitter receptor on the muscle, and green is Schwann cells.
Image courtesy of Hiroshi Nishimune.
Jose Ramirez-Vasquez 2
Alpha Motor Neuron
This type of neuron is responsible fort the innervations of the extrafusal fibers (Bear et al. 2006).
Gamma Motor Neuron
This lower neuron sends the motor innervations to the intrafusal fibers (Bear et al. 2006).
Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine
Physiology
Gamma and Alpha motor neurons can be simultaneously activated by commands from the brain
(Bear et al. 2006).
In a muscle contraction, alpha motor neurons make the extrafusal fibers contract, and the muscle shortens. The Gamma motor neurons innervate the intrafusal muscle fiber at the two ends of the muscle spindle, and it produces a contraction of the two poles of the muscle spindle (Bear et al.
2006).
References
1.
Bear, Mark F., Connors, Barry W., Paradiso Michael A. (2006). Neuroscience:
Exploring the Brain. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD, 857 pp.
2.
Institute for Neurological Disorders http://www.indkc.org/images.html 8/29/09
3.
Wada T, Honda M, Minami I, Tooi N, Amagai Y, et al. (2009) Highly Efficient
Differentiation and Enrichment of Spinal Motor Neurons Derived fromHuman and
Monkey Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 4(8): e6722. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006722