The Organization of Living Things Notes
advertisement

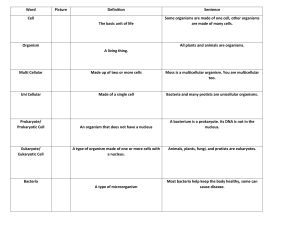
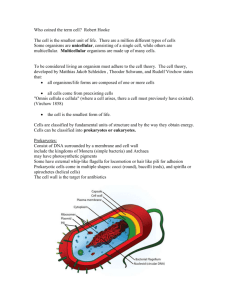
The Organization of Living Things: Section 4.3 What is an organism? - A living thing Anything that can perform life processes by itself Unicellular _____________________ cell Organisms Prokaryotes (no nucleus) : __________and archaea _______________ (have a nucleus) like yeasts, some algae, some protists Multicellular - Made of ______________________ cells Organisms - Plants and ____________________ - ______________________ size - _______________________ life - Specialization: each cell has a _______________job to do How are multicellular Level 1: ______________________ organisms Animals: heart cells, bone cell, brain cells organized? Plants: guard cells, root cells Level 2: ______________________ (a group of cells working together) Animals: nerve tissue, muscle tissue Level 3: ______________________ (a group of tissues working together) Animals: heart, stomach, brain Plants: leaf, stem, roots Level 4: ______________________ (a group of organs working together) Animals: digestive, cardiovascular Level 5: ______________________ (all of the organ systems working together) Examples: human, cat, oak tree, honey bee Differentiation or - In ______________________ organisms, cells differentiate or Specialization become specialized. - They will have a ______________________ job to do Example: Blood cells carry oxygen and muscle cells contract - Once they differentiate, they _______________ become other cells - Only differentiated _________________ cells can become a new cell Example: a leaf cell can become a root cell