TURN IN your Test Corrections! In your Bellwork section:
advertisement

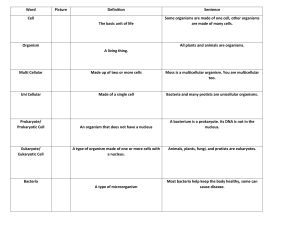
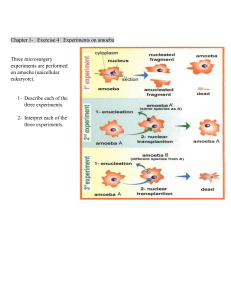
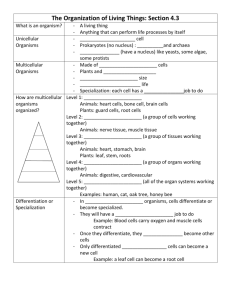
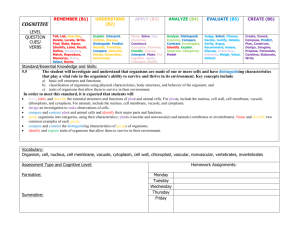
TURN IN your Test Corrections! In your Bellwork section: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Compare and Contrast “water” and a “plant” How are they the same? How are they different? What makes a “water” a “water?” What makes a “plant” a “plant?” We will begin class 4 minutes after the bell Please work the whole 4 minutes! It’s going to be a great year! -Mrs. Pollard- 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. All living things are composed of cells Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living things New cell are produced from existing cellsreproduction and development All organisms require energy to carry out certain processes. (metabolism) Response to their environment –all organisms must react to their environment to survive. Brainstorm ◦ characteristics these cells have in common ◦ characteristics these cells have different Classify the cells you see into two or three groups ◦ Explain what characteristics you used to put each cell in a particular group ◦ Give a name for each group Use observations to write a definition of a “cell” Genetic material not contained in a nucleus Smaller Simpler; less complicated Examples: ◦ Archaebacteria – extreme environment ◦ Eubacteria – E.coli Genetic material is contained in a nucleus ◦ Separated from rest of cell Complex Larger Variety ◦ Single-cell organisms – Amoeba ◦ Multi-cell organisms – plants, animals, fungi, protista Plant Cell Prokaryote Cells No nucleus Eukaryote Cell Single-cell organism Picture of an amoeba Eukaryote Cell Multi-cellular organism Picture of a human cell