Perineum Quiz 2 Answers
advertisement

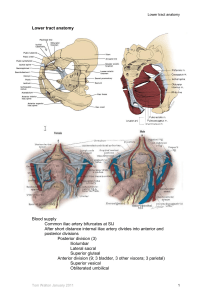
Perineum Quiz 2 w/ answers 1. Each hypogastric nerve (that connects the superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses) crosses the common iliac artery and then the medial surface of the __________. At the point of crossing, the nerve and vessel(s) are separated by ___________. A) internal iliac artery or its branches --- peritoneum B) internal iliac artery or its branches --- extraperitoneal connective tissue C) external iliac artery --- peritoneum D) external iliac artery --- extraperitoneal connective tissue Correct Answer(s): B 2. The __________ can be palpated in a rectal examination (insertion of a gloved finger into the anal canal and rectum). A) contents of the rectovesical or rectouterine pouch B) perineal body (central tendon of the perineum) C) urogenital diaphragm D) ischial spines E) All of the above are correct. F) Only answers B and C above are correct. Correct Answer(s): 3. E The ________ nerve is responsible for the vaginal pain that accompanies childbirth. In order to anaesthetize this nerve, the obstetrician should use the _________ as a landmark for injection of local anaesthetic. A) genitofemoral --- ischial spine B) genitofemoral --- pubic tubercle C) pudendal --- ischial spine D) pudendal --- pubic tubercle Correct Answer(s): C 4. Dr. Marv A. Louse performed a hysterectomy because of a cancerous lesion on the wall of a patient's uterus. The fundus, body and cervix of the uterus were removed, but the uterine tubes were transected and left in place with the ovaries. In order to perform this procedure, it was necessary to cut the A) suspensory ligament of the ovary with the ovarian artery. B) (round) ligament of the ovary with the ovarian - uterine arterial anastomosis. C) transverse / lateral cervical / cardinal ligament with the uterine artery. D) All of the above are correct. E) Only answers B and C above are correct. Correct Answer(s): E 5. Following the removal of his prostate, a patient may be unable to have an erection. The reason is that the part of the inferior hypogastric plexus that surrounds the prostate contains nerves that carry A) afferent axons from the skin of the glans penis. B) axons that innervate the bulbospongiosus muscle. C) preganglionic sympathetic axons that cause dilation (relaxation) of the penile branches of the internal pudendal artery. D) preganglionic parasympathetic axons that cause dilation (relaxation) of the penile branches of the internal pudendal artery. Correct Answer(s): D 6. During the routine examination of a male patient, Dr. I.B. Noitall palpated enlarged superficial inguinal lymph nodes. One possible cause is an infection in the lower extremity. Others are an infection or metastasis from a primary tumor in the A) scrotum B) testis C) anal canal inferior to the pectinate (dentate) line D) All of the above are correct. E) Only answers A and C above are correct. Correct Answer(s): E 7. The __________ muscle contributes to the lateral wall of the ischiorectal (ischioanal) fossa. A) piriformis B) obturator internus C) external anal sphincter D) coccygeus E) levator ani Correct Answer(s): B 8. The parietal pelvis fascia that lines the floor and walls of the pelvic cavity is continuous with the __________ of the abdomen. A) transversalis fascia B) Colles' fascia C) Scarpa's fascia D) peritoneum E) Camper's fascia Correct Answer(s): A 9. The __________ muscle is in the superficial perineal space (pouch). A) ischiocavernosus B) sphincter urethrae C) coccygeus D) puborectalis E) All of the above are correct. F) Only answers A and B are correct. Correct Answer(s): A 10. All of the uterus superior to the __________ is called the _________. A) pelvic diaphragm --- fundus B) internal os (opening) of the cervix --- isthmus C) entrance of the uterine tube ---fundus D) external os (opening) of the cervix --- isthmus Correct Answer(s): C 11. The seminal vesicles lie directly ________ to the __________. A) posterior --- base of the bladder (trigone) B) superior --- apex of the bladder C) inferior --- prostate gland D) Both answers A and B are correct. Correct Answer(s): A 12. The ___________ can be used to mark the junction of the rectum and anal canal. A) inferior end of the sigmoid mesentery B) puborectalis C) lower transverse rectal fold D) anal valves Correct Answer(s): B 13. The ________ artery passes _________ before supplying most of the blood to the _____________. A) umbilical --- across the pelvic brim --- inferior portion of the bladder B) internal pudendal --- around the ischial spine --- corpora cavernosus erectile tissue C) uterine --- in the base of the broad ligament --- ovaries D) vaginal --- superior to the ureter --- bulb of the vestibule Correct Answer(s): B 14. During prenatal development, the _________ pass(es) through the opening in the transversalis fascia that becomes the deep inguinal ring. A) ovarian artery and vein B) ilioinguinal nerve C) processus vaginalis D) scrotal lymph vessels Correct Answer(s): C 15. __________ axons cause contraction of a muscle that either elevates the testis or decreases the surface area of the scrotum. A) Somatic B) Sympathetic C) Parasympathetic D) All of the above are correct. E) Only answers A and B above are correct. F) Only answers B and C above are correct. Correct Answer(s): E 16. The membranous part of the urethra passes through all or a portion of the _________ and is the __________ dilatable part of the urethra. A) bulb of the penis --- least B) bulb of the penis --- most C) corpus spongiosum --- least D) corpus spongiosum --- most E) urogenital diaphragm --- least F) urogenital diaphragm --- most Correct Answer(s): E 17. A strangulated indirect inguinal hernia lies in the inguinal canal. The surgeon will gain access to the lateral one third of the canal with an anterior approach to reduce the hernia and prevent its reoccurrence. The scalpel must pass superior to the inguinal ligament through skin, superficial fascia and the _________ layer of the anterior abdominal wall. A) aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique B) internal abdominal oblique muscle C) transversus abdominus muscle D) All of the above are correct. E) Only answers A and B are correct. F) No other layer of the wall will be cut. Correct Answer(s): E 18. A strangulated indirect inguinal hernia lies in the inguinal canal. The surgeon will gain access to the lateral one third of the canal with an anterior approach to reduce the hernia and prevent its reoccurrence, as described in the previous question. The _________ is most endangered in this procedure because of its location in the anterior wall of the lateral third of the inguinal canal. A) genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve B) inferior epigastric vessels C) vas deferens D) ilioinguinal nerve E) aberrant obturator artery Correct Answer(s): D 19. When performing a normal intravenous urogram (IVU), in which sterile, water-soluble, iodine-containing contrast is administered via a peripheral vein, the part of the urinary collecting system that will be visualized before any other is: A) the bladder. B) the major calyx. C) the renal artery. D) the minor calyx. Correct Answer(s): D